Royal Caribbeana major player in the cruise industry, joins forces with the Caribbean Tourism Organization (CTO) to promote the sustainable growth of tourism in this paradise region. This month, a landmark event took place in Miami, the Caribbean Weekend, bringing together tourism ministers, executives and other key players to discuss the opportunities and challenges facing the sector.
An iconic tourism summit
The event, entitled “Envisioning Caribbean Tourism: An Iconic Summit”, was held on board Royal Caribbean‘s latest ship, the icon of the Seas. The meeting initiated vital discussions on job creation, sustainability and community engagement. Michael Bayley, President and CEO of Royal Caribbean, opened the proceedings, emphasizing the importance of the cruise industry to the Caribbean economy.
” The Caribbean is the soul of Royal Caribbean. Around 60% of our business comes from this region,” he said, emphasizing the deep ties between the company and the islands.
Royal Caribbean's commitment to sustainability
Sustainability is a central theme of this initiative. Bayley reaffirmed Royal Caribbean’s commitment to reducing its ecological footprint. Among the initiatives presented was the use of biofuels and liquefied natural gas (LNG) to power its ships. This demonstrates a commitment to meeting environmental challenges while continuing to support the local economy.
Ian Gooding-Edghill, Chairman of the CTO and Barbados’ Minister of Tourism and International Transport, also stressed the importance of cross-sector collaboration in achieving these goals. “We need to work together to reinvent the future of tourism in the Caribbean,” he said.

Employment opportunities and local sourcing
Royal Caribbean is also committed to creating employment opportunities for the people of the Caribbean. Bayley has highlighted the need to improve supply chain systems to support local producers. Working hand-in-hand with local ministries, the company aims to develop cooperatives that would facilitate the supply of fresh produce for its ships.
He also mentioned the American Caribbean Maritime Foundation’s cadet program, which enables talented young people to train and take part in the maritime industry. The story of a female officer from the Bahamas, who sailed aboard the Icon of the Seas, was particularly inspiring for participants.
The importance of partnerships
The summit highlighted the vital role of partnerships in transforming the tourism industry. Dona Regis-Prosper, Secretary General of the CTO, expressed her gratitude to Royal Caribbean for its ongoing commitment. She said, “This iconic summit underscores the power of partnerships and collaboration. We need to reimagine our approach to tourism development.”
Royal Caribbean is also committed to strengthening exchanges and communication between the industry’s various stakeholders. This includes a better understanding of the needs and challenges of Caribbean communities, to ensure that tourism development benefits all.
Royal Caribbean's vision for the future
As Royal Caribbean prepares to launch its next ship, Star of the Sea, Bayley reassured attendees that the Caribbean will continue to be at the heart of its operations. The company is committed to investing in the region, creating a future where sustainable growth and the economic well-being of the Caribbean are paramount.
Supporting sustainability initiatives and promoting local culture are key elements of this vision. This involves not only financial investment, but also a long-term commitment to local communities.
A promising future for tourism
The Miami meeting was a pivotal moment for the Caribbean tourism sector. Thanks to the collaboration between Royal Caribbean and the CTO, new opportunities for sustainable growth are on the horizon. The discussions held at the summit should serve as a springboard for future initiatives, aimed at ensuring that tourism in the Caribbean is both economically viable and environmentally friendly.
By further integrating local stakeholders into the development process and adopting sustainable practices, Royal Caribbean is proving that it is possible to combine pleasure and responsibility. The future of tourism in the Caribbean looks bright, and with a strong commitment and solid partnerships, it’s likely that this region will continue to shine on the world tourism stage.
Christmas in the Caribbean is a unique time of celebration, filled with colorful traditions and tasty dishes. The Caribbean islands are known for their festive atmosphere, and cuisine is at the heart of these festivities. The magic of Christmas in this region is palpable, with bright decorations, joyful carols and, above all, dishes that awaken the senses. In this article, we’ll explore four iconic recipes that make Christmas unforgettable: lambi or grilled fish with sosé, Great cake, Christmas ham tuiles and nwel ham.
1. Lambi or grilled fish with sosé
Ingredients
- Lambi or fish of your choice
- Local spices
- Tomatoes
- Peppers
- Onions
Preparation
- Cleaning the lambi: If you use lambi, clean it thoroughly to remove all sand and impurities.
- Marinade: Marinate lambi or fish with local spices to enhance flavours.
- Grilling: Grill on the barbecue or in a frying pan, taking care to cook thoroughly.
- To prepare the sauce: In a saucepan, sauté the onions, tomatoes and peppers with the spices, then add water and simmer until cooked through.
This tasty dish, often served with rice or vegetables, is a staple of Christmas tables in the Caribbean, symbolizing the richness of local maritime resources.

2. Great cake
Ingredients
- 1/2 cup dried fruit
- 113.4 g nuts (almonds or peanuts)
- 227 g sugar
- 227 g flour
- 6 eggs
- Spices (cinnamon, nutmeg, cloves)
Preparation
- Fruit preparation: Wash and dry the fruit, then soak it in alcohol for several months for a rich taste.
- Caramel: Melt the sugar to a caramel-like consistency. Add it to the mixture.
- Mixing the ingredients: In a large bowl, mix the sugar and margarine, then add the eggs one by one.
- Adding fruit and nuts: Add fruit and nuts to the dough.
- Baking: Pour into a baking tin and bake at 300°F for about 2 hours 30 minutes.
The large cake, often rich in flavor and alcohol, is a tradition that brings warmth and conviviality to festivities. It is often served at family gatherings and is a symbol of Caribbean hospitality.

3. Nwel ham
Ingredients
- 1 Christmas ham
- Red sugar
- Spicy sauce (cinnamon, nutmeg, etc.)
- Pineapple
Preparation
- Defrosting: Make sure the ham is completely defrosted before starting to prepare it.
- Caramel: Melt the sugar in a pan until you obtain a golden caramel.
- Brushing: Brush the ham with the caramel and add the spicy sauce.
- Baking: Bake at 180°C for 30 to 40 minutes, basting regularly to keep the ham juicy.
Jamon nwel is usually the main course at Christmas meals, representing celebration and family unity. It is usually served with side dishes such as mashed potatoes or roasted vegetables.

4. Christmas ham tiles
Ingredients
- Brick pastry
- Christmas ham
- Unsalted butter, melted
Preparation
- Dehydrating ham: Dehydrate the ham and crumble it into fine crumbs to obtain the perfect texture.
- To prepare the brick pastry sheets: Place the ham crumbs in brick pastry sheets, previously brushed with melted butter.
- Cooking: Brown the tiles in a non-stick frying pan or in the oven until crisp and golden.
These crunchy tuiles are the perfect start to a festive meal, adding a crunchy touch to any celebration. Served with a spicy sauce or fruit jam, they’re sure to delight your guests.

The flavors of Christmas in the Caribbean are a sensory experience that delights the taste buds. Whether it’s crispy ham tuiles, savory lambi, rich grand gâteau or fragrant nwel ham, each dish tells a story of tradition and conviviality. Not only are these recipes delicious, they also bring invaluable warmth to family Christmas gatherings. Each of these culinary creations evokes memories and shared moments, making every Christmas even more memorable.
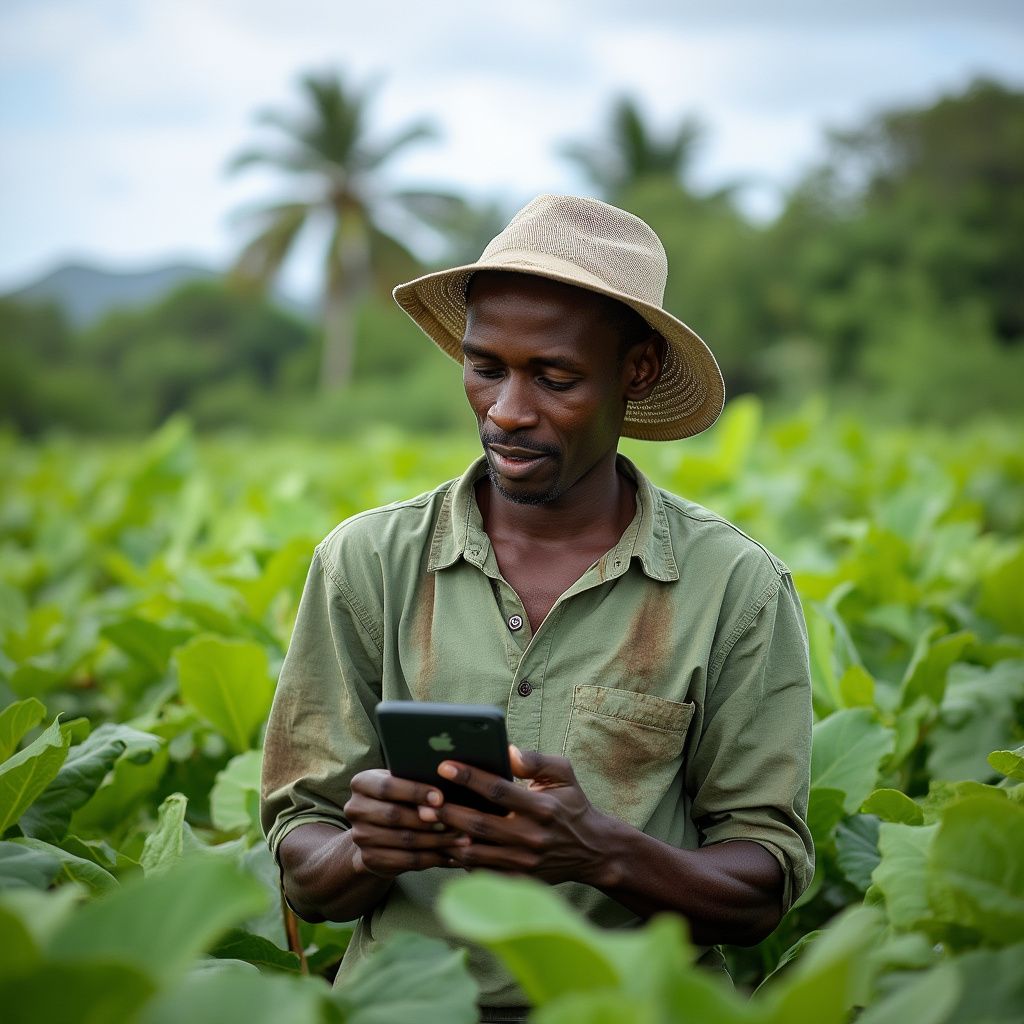
The Ministry of Agriculture of Barbados, in partnership with the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), hosted a workshop on the theme “Optimizing Agricultural Production through High-Precision Digital Crop Management Systems.” This event highlighted the importance of “precision agriculture in Barbados” and its potential to transform the agricultural landscape of the island.
An Essential Workshop for the Future of Precision Agriculture in Barbados
This initiative took place on Monday, December 2, 2024, in the Ministry’s Conference Room, located at Graeme Hall, Christ Church, Barbados. The workshop aimed to strengthen “precision agriculture”, which was crucial for sustainable development and food security in Barbados. By bringing together stakeholders from various sectors, the workshop served as a platform for sharing knowledge, experiences, and best practices in precision agriculture.
Project Background
The project, funded under the FAO Technical Cooperation Program, aimed to promote “precision agriculture” in Barbados and increase productivity through the integration of advanced digital crop management systems. The goal was to harmonize new technologies with traditional farming methods. This helped strengthen the agricultural sector of Barbados, ensured food security, and contributed to sustainable development.
In addition, the project focused on training farmers and agricultural technicians in the use of digital tools and technologies that could enhance crop management. By integrating these technologies, farmers were able to better monitor crop health, optimize resource usage, and ultimately improve yields.
Presentations by Recognized Experts in Precision Agriculture in Barbados
The workshop featured several presentations by recognized experts in the field. Among the speakers, Timothy Drakes, Project Focal Point at the Ministry, presented an analysis of the current state of vegetable cropping systems in Barbados.
Jervis Rowe, an international consultant for FAO, discussed the advantages of protected cultivation systems for vegetable production. These systems were particularly relevant in the context of climate change and helped farmers mitigate risks associated with unpredictable weather patterns. predictable weather patterns.
Melvin Medina Navarro, the FAO Project Lead Technical Officer, provided a comprehensive overview of the project’s log-frame, outputs, and activities, highlighting the expected impact of the project on local agricultural practices.
Discussions on Cross-Cutting Issues Affecting Precision Agriculture in Barbados
Additionally, discussions on cross-cutting issues such as gender equality, environmental considerations, grievance mechanisms, and communication strategies were led by Anne Desrochers, a specialist in plant production and protection at FAO. These discussions were essential for encouraging an integrated approach to developing “precision agriculture” in Barbados.
By addressing these issues, the workshop aimed to create an inclusive environment where diverse perspectives could contribute to the advancement of precision agriculture. It was crucial that all stakeholders, including women and marginalized groups, had a voice in shaping the future of agriculture in Barbados.
Importance of Precision Agriculture in Barbados
This workshop represented a valuable opportunity for stakeholders in Barbados to engage in constructive dialogue, ask questions, and contribute to the success of this vital project for the future of agriculture in the Caribbean.
“Precision agriculture” is a major issue that allows farmers to optimize their resources, increase productivity, and address environmental challenges. By integrating advanced technologies such as drones, sensors, and management software, farmers were able to make informed decisions that promoted sustainability. This not only enhanced productivity but also ensured that farming practices did not compromise the health of the environment.
As the agricultural sector in Barbados faced challenges such as climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity, the adoption of precision agriculture techniques became crucial. Farmers benefited from data-driven insights that helped them make better decisions regarding planting, irrigation, and pest management.

The workshop organized by the Ministry of Agriculture of Barbados and FAO was a crucial step towards enhancing “precision agriculture in Barbados.” By uniting the efforts of experts and stakeholders, this event paved the way for more sustainable and productive agriculture, thereby ensuring a better future for farmers and consumers in the Caribbean.
In summary, the integration of precision agriculture practices represented not just an opportunity for increased productivity but also a commitment to sustainability and food security in Barbados. We encourage all interested parties to reflect on the insights gained during this workshop to further explore the potential of precision agriculture in transforming the agricultural landscape of the region.
Chukka Caribbean Adventures, with its stunning white sand beaches, turquoise waters, and rich biodiversity, represents a dream destination for many travelers. At the heart of this enchanting region, one company stands out for its commitment to sustainable tourism and customer experience: Chukka Caribbean Adventures.
Recently, Chukka was honored as the “World’s Leading Destination Experiences 2024” at the 31st World Travel Awards, celebrating its role as a leader in the adventure tourism industry. This article explores the impact of Chukka Caribbean Adventures on the tourism sector, its innovative approach, and the reasons it has become a benchmark in tourist experiences.

A Commitment to Sustainable Tourism
Chukka Caribbean Adventures was founded to provide authentic experiences while preserving the environment and supporting local communities. The company is devoted to protecting the fragile ecosystems of the Caribbean by integrating sustainable practices into every aspect of its operations. This includes using eco-friendly materials, reducing waste, and raising customer awareness about the importance of conservation.
Marc Melville, the CEO of Chukka, stated: “Our mission is to create extraordinary experiences that reflect the beauty and culture of the Caribbean while respecting our environment.” This commitment to sustainability has allowed Chukka to stand out in an increasingly competitive sector, where travelers seek options that positively impact the communities they visit.
Diverse and Immersive Experiences
Chukka Caribbean Adventures offers a wide range of activities that go beyond simple tourist excursions. Whether outdoor adventures, cultural immersions, or adrenaline-pumping activities, each experience is designed to foster a deep connection with the environment and local communities.
Eco-Adventures
The eco-adventures offered by Chukka allow travelers to discover the unique biodiversity of the Caribbean. From kayaking through mangroves to hiking in tropical forests, each activity is guided by experts who share their knowledge of local wildlife and flora. These educational experiences enable visitors to understand the importance of preserving these ecosystems and encourage responsible tourism practices.
Cultural Immersions
The cultural aspect of Chukka’s offerings is equally enriching. Visitors can participate in artisanal workshops, explore local cuisine, or attend traditional music and dance performances. These immersions not only entertain; they also support local artisans and artists, creating a virtuous cycle where tourism directly benefits communities.
Thrilling Activities
For thrill-seekers, Chukka Caribbean Adventures offers exhilarating activities such as zip-lining, rafting, and scuba diving. These experiences are designed to provide an adrenaline rush while adhering to the strictest safety standards. By integrating these activities into a sustainable framework, Chukka ensures that visitors can enjoy adventure without compromising environmental integrity.
The Impact of the World Travel Awards
Receiving the title of “World’s Leading Destination Experiences 2024” at the World Travel Awards is a significant achievement for Chukka Caribbean Adventures. These awards, often compared to the “Oscars of Travel,” recognize leaders who innovate and drive excellence in the tourism sector. This distinction shines a light not only on the hard work of the Chukka team but also on the growing importance of sustainable tourism globally.
A Well-Deserved Recognition
This recognition crowns over 40 years of experience in the adventure tourism sector. Since its inception in 1983, Chukka has adapted to market changes and consumer expectations while remaining true to its core values. The company’s ability to innovate while preserving its commitment to sustainability is what places it at the forefront of the industry.
In summary, Chukka Caribbean Adventures is more than just a tourism company; it is a model of success in the field of sustainable tourism. Through its commitment to environmental protection and support for local communities, Chukka offers experiences that leave a positive footprint on travelers and the Caribbean region.
By winning the title of “World’s Leading Destination Experiences 2024,” Chukka confirms its status as a leader in the tourism industry and inspires other companies to follow its example.
For travelers seeking unique and responsible adventures, Chukka Caribbean Adventures represents an essential option. Whether you’re looking for cultural immersion, an escape into nature, or an adrenaline rush, Chukka invites you to discover the best of the Caribbean while respecting the environment and supporting local communities.
Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean has become an essential aspect of the region’s development. With its rich cultural heritage, breathtaking natural landscapes, and unique traditions, the Caribbean attracts millions of visitors each year. The promotion of these cultural elements as tourist attractions is crucial for preserving local identity while meeting the needs of visitors. This article examines the challenges and opportunities associated with sustainable tourism in the Caribbean, emphasizing cultural heritage’s role in enhancing tourist experiences.
The Importance of Cultural Heritage in Tourism
Cultural heritage encompasses the traditions, customs, arts, and historical narratives that define a community. In the Caribbean, this heritage is diverse and multifaceted, reflecting the region’s complex history influenced by Indigenous peoples, European colonization, African cultures, and more. Tourists are drawn to the Caribbean not only for its stunning beaches but also for its vibrant cultures, making cultural heritage a significant driver of tourism.
By integrating cultural experiences into tourism offerings, destinations can attract visitors seeking authentic experiences. This approach not only enriches the tourist experience but also fosters a deeper appreciation for local cultures, leading to a more sustainable form of tourism.
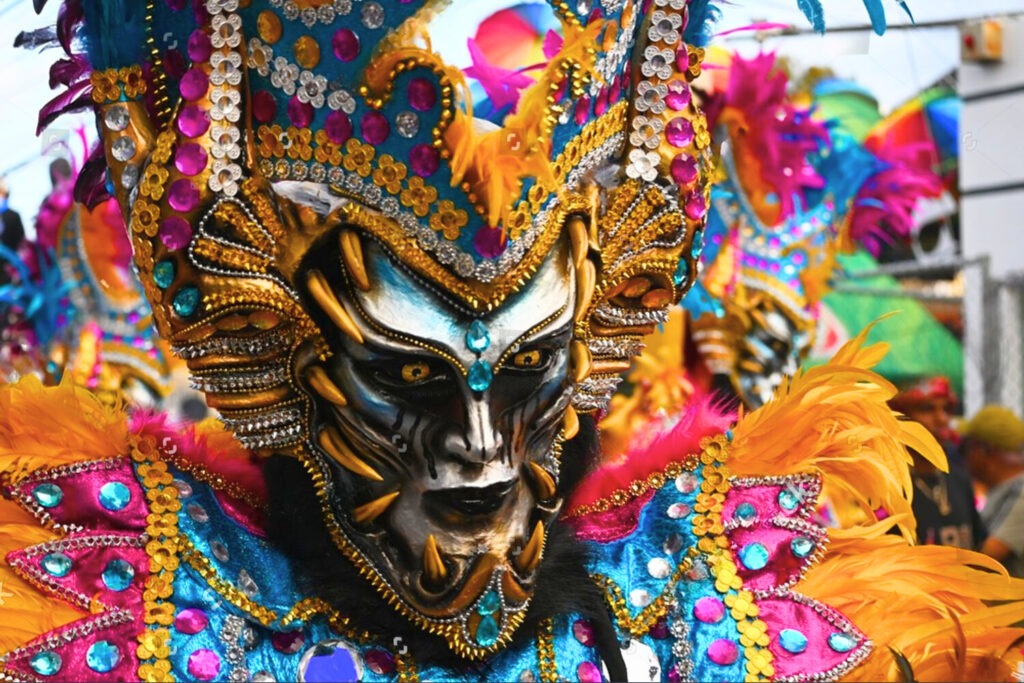
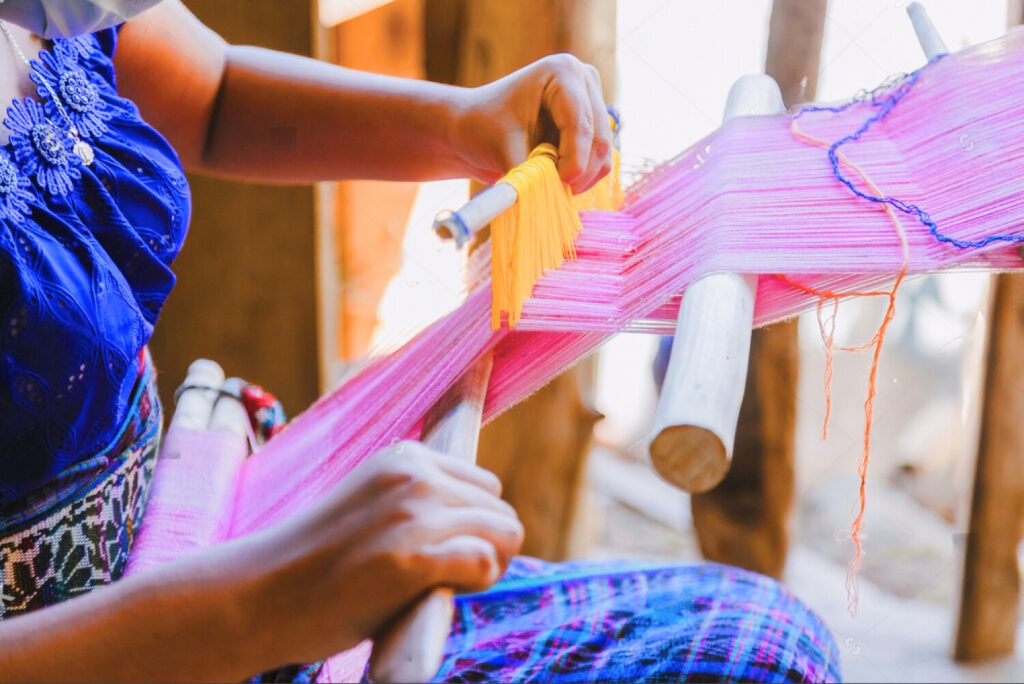


Challenges of Sustainable Tourism
Pressure on Cultural Resources
The influx of tourists can lead to excessive exploitation of cultural resources, such as festivals, traditional events, and historical sites. This pressure can compromise the authenticity and longevity of local cultural practices. Destinations often face the dilemma of balancing tourism growth with the preservation of their unique cultural identities.
For instance, traditional festivals may be altered to cater to tourist expectations, potentially losing their original significance. This commercialization can lead to a superficial understanding of the culture, with visitors experiencing a version that is tailored for mass consumption rather than genuine engagement.
Erosion of Cultural Identity
Mass tourism can sometimes result in the commercialization of traditions, leading to a dilution of cultural identity. Local practices may be adapted to meet tourist expectations, creating a disconnect between genuine traditions and those presented to visitors. The risk of cultural appropriation also arises, where elements of local culture are taken out of context and used superficially by outsiders.
Moreover, younger generations may feel less inclined to engage with their heritage if they perceive it as something primarily for tourists. This generational shift can threaten the transmission of cultural knowledge and practices, jeopardizing the long-term sustainability of local traditions.
Infrastructure and Management
Many Caribbean destinations lack adequate infrastructure to manage the flow of tourists interested in culture. This can result in challenges related to site management, preservation of artifacts, and respect for traditional practices. Insufficient funding for the maintenance of cultural sites can lead to deterioration, further diminishing their appeal to tourists.
Effective management strategies are essential to ensure that cultural sites can accommodate visitors without compromising their integrity. This may involve training local guides, implementing visitor limits, and developing educational programs that emphasize the importance of conservation.
Vulnerability to Environmental Changes
Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, can destroy cultural and historical sites, jeopardizing the heritage that attracts tourists. The resilience of these sites is essential to ensure continued tourist appeal. Climate change poses a significant threat to the Caribbean, with rising sea levels and increased storm frequency impacting both the environment and cultural heritage.
Investments in disaster preparedness and recovery are crucial for safeguarding these sites. By building resilient infrastructures and promoting sustainable tourism in the Caribbean , destinations can better withstand environmental challenges.
Opportunities of Sustainable Tourism
Highlighting Local Traditions
Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean provides a platform to promote the arts, music, dance, and festivals that are central to Caribbean identity. Events such as Carnival in Trinidad and Tobago, Junkanoo in The Bahamas, and Reggae festivals in Jamaica showcase the vibrant cultural tapestry of the region. By integrating authentic cultural experiences into tourist offerings, visitors can discover the richness of the Caribbean while supporting local communities and patricipate to the sustainable tourism in the Caribbean.
Local artisans can also benefit from Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean. By encouraging the purchase of handmade crafts and artworks, tourism can contribute to preserving traditional skills and providing economic opportunities for local artists.
Education and Awareness
Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean offers an opportunity to raise visitor awareness about cultural and environmental issues. Guided tours, workshops, and cultural events help tourists develop a deeper understanding of local realities and the importance of heritage preservation. Educational initiatives can empower visitors to engage more meaningfully with the culture, fostering respect and appreciation.
For example, cultural immersion programs that involve community members can provide tourists with insights into daily life, traditions, and the challenges local communities face. This engagement can enhance the overall visitor experience, making it more impactful and memorable.
Community Economic Development
Focusing on culture as a tourist attraction allows local communities to benefit directly from the tourism economy. This encourages the creation of artisanal businesses, cultural tours, and services related to the arts, thus stimulating local economic development. Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean can empower communities by providing job opportunities and fostering entrepreneurship.
Moreover, when tourists spend money on local products and services, the economic benefits circulate within the community, contributing to its overall well-being. This model promotes a more equitable distribution of tourism revenues, reducing reliance on external entities.
Sustainable Partnerships
Developing partnerships among governments, cultural organizations, and the private sector is crucial for promoting Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean. These collaborations can support initiatives that preserve cultural heritage while providing enriching experiences for visitors. By working together, stakeholders can create a comprehensive approach to Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean that addresses environmental, social, and economic dimensions.
For instance, partnerships can facilitate joint marketing efforts that highlight cultural events, promoting them to a broader audience. Collaborative projects can also enhance the infrastructure necessary for managing tourism sustainably, ensuring that cultural sites are well-maintained and accessible.
To conclude, sustainable tourism in the Caribbean presents both challenges and opportunities, particularly in terms of valuing culture as a tourist attraction. By adopting environmentally respectful practices and highlighting local traditions, the region can preserve its unique heritage while offering memorable experiences to visitors. A collective commitment from tourism stakeholders, local communities, and governments is essential to create a development model that benefits all, celebrating the diversity and authenticity of the Greater Caribbean.
The path forward involves recognizing the intrinsic value of culture and heritage in tourism, fostering a sense of pride among local communities, and ensuring that tourism serves as a force for positive change. By embracing sustainable tourism practices, the Caribbean can continue to thrive as a premier destination while honoring its rich cultural legacy.
BARBADOS
Land of Rum
Barbados is an island nation celebrated for its rich history, cultural diversity, and natural beauty. It’s known for its dynamic landscape, ranging from lush, verdant terrains to breathtaking coastlines.
As a premier tourist destination, Barbados offers an array of attractions and activities catering to various interests.
It is uniquely positioned in the southeastern Caribbean, boasting a warm climate with an average temperature of 30°C. The island is distinguished by its diverse environment, from the tranquil Caribbean Sea on the west to the more turbulent Atlantic Ocean on the east.

Geographic and Geological Overview
A Geographic Snapshot
Size : 166 square miles; approximately 21 miles long and 14 miles wide.
Capital: Bridgetown, located on the southwestern coast.
High Point: Mount Hillaby at 340 meters (1,115 feet) above sea level.
Population: Approx. 287,000 as of 2020.
Vegetation: Dominated by scrubland and coastal mangroves rather than lush, dense tropical forests.
Water Bodies: Surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean; known for its beautiful beaches rather than significant rivers.
Agriculture: Historically dependent on sugarcane, but now diversified; tourism is the primary economic driver.
Geological Features
Geology: it is a coral island, not volcanic, with limestone formations and relatively flat terrain.
Natural Wonders: Notable for its beautiful coral reefs and the Harrison’s Cave.
Cultural Tapestry
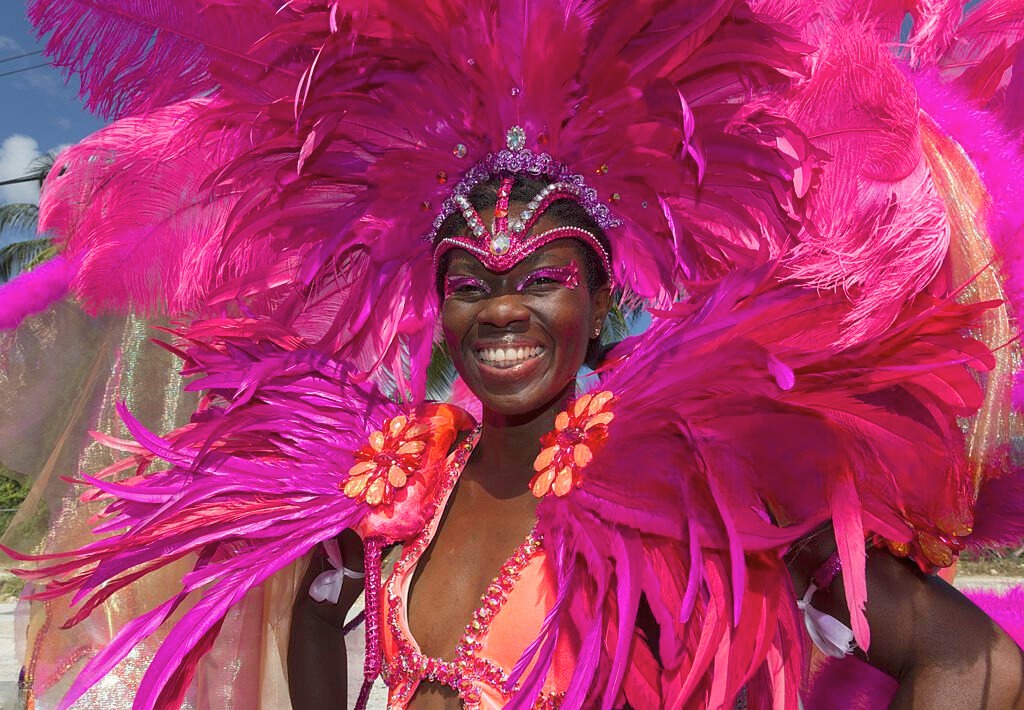
The Crop Over
The island’s culture is a rich blend of African, European, and local influences. Signature events like the Crop Over Festival celebrate the end of the sugar cane season with vibrant parades and music, symbolizing the deep-rooted history and community spirit of the island.

Rally Barbados
This is the island’s premier motorsport event, drawing participants and spectators from across the globe. It’s a significant part of Barbados’ sports-tourism calendar, featuring exciting tarmac rally racing. Highlight the event dates, the main attractions such as the King of the Hill prelude event, and its role in showcasing Barbados’ vibrant community and scenic roads.

Local Cuisine
Bajan’s Cuisine Highlight
Barbadian cuisine, also known as Bajan cuisine, is noted for dishes such as Cou Cou and Flying Fish, the national dish that reflects the island’s culinary arts and access to fresh seafood.
The Barbados Food and Rum Festival further showcases the island’s gastronomy, featuring local and international chefs.




Economy and Infrastructure
Economic Resilience and Challenges
Barbados is classified as a high-income country with one of the highest incomes per capita in the Caribbean. The economy is diversified, anchored primarily by tourism and offshore banking.
The backbone of the Barbadian economy, tourism significantly influences overall economic health, contributing to around 12% of GDP in recent years. The sector is supported by excellent infrastructure, including well-maintained roads, modern airports, and advanced telecommunications.
The island is a globally recognized offshore jurisdiction, offering a regulatory environment that attracts international business and financial services. This sector contributes notably to government revenue and foreign exchange.
The island boasts a well-developed public infrastructure, including a reliable road network, extensive water distribution systems, and comprehensive health and educational facilities. Recent government initiatives aim to boost public sector efficiency and infrastructural resilience.
Despite its strengths, the Barbadian economy faces high public debt, necessitating fiscal adjustments and economic reforms.
The island is advancing in environmental sustainability, with investments in coastal infrastructure to combat erosion and initiatives to promote renewable energy sources, positioning it as a leader in ecological resilience in the Caribbean.
The island is also a global leader in rum production, with historic distilleries such as Mount Gay, which highlight the island’s long-standing tradition of rum making.

Historical Insights
From Settlement to Sovereignty
Barbados boasts a rich historical tapestry that has been shaped by various influences throughout the centuries. From its early settlement by the Arawak and Carib peoples to its later colonization by the British in 1627, the island’s history is a vivid narrative of resilience and transformation. Here are some key historical insights :
Early Settlements: Before European colonization, the island was inhabited by Indigenous peoples, primarily the Arawak and Carib, who called the island ‘Ichirouganaim’.
Colonial Era: Claimed for King James I of England in 1625, the island became an English and later British colony. The island played a significant role in the sugar industry, with sugar plantations powered by enslaved Africans becoming the backbone of its economy.
Emancipation and Cultural Shifts: The abolition of slavery in 1834 marked a turning point. Freed slaves began to shape their own communities and cultures, contributing significantly to the social fabric of the island.
Path to Independence: Throughout the 20th century, the island moved towards self-government, achieving full independence from the United Kingdom on November 30, 1966. This day remains a national holiday celebrated as Independence Day.
Modern Developments: In recent decades, the island has developed a mixed economy with tourism, manufacturing, and agriculture as key sectors. The island is known for its stable political environment and high standards of living compared to other Caribbean nations.
Barbados’ historical journey from a colonial outpost to a thriving independent nation is a testament to the enduring spirit and resilience of its people. This rich history continues to be reflected in the island’s cultural practices, architecture, and societal norms, making it a unique study in Caribbean history and heritage.
What Makes Barbados So Unique
- Political Independence: Barbados’ transition from a British colony to an independent nation in 1966, and its move to become a republic in 2021, underline its unique political journey in the Caribbean.
- Economic Diversification: Unlike many Caribbean nations, the island has a diversified economy not solely reliant on tourism but also bolstered by manufacturing and financial services.
- Cultural Heritage: The island’s rich history is reflected in its music, dance, and festivals, especially the Crop Over Festival which has roots in the colonial sugar cane harvest.
- Environmental Initiatives: Barbados is proactive in environmental protection, with significant investments in renewable energy and coastal rehabilitation projects to combat climate change impacts.
- Historical Sites: Home to George Washington House and the UNESCO World Heritage site of Historic Bridgetown and its Garrison, the island offers a deep dive into colonial history.
- Flourishing Arts Scene: The island has a vibrant arts scene, including the renowned NIFCA performing arts festival which showcases local music, dance, and drama.
- Advanced Infrastructure: Barbados boasts well-developed infrastructure, including modern healthcare facilities, international airports, and a reliable road network.
- Educational Hub: With a high literacy rate and reputable institutions such as the University of the West Indies, the island is considered an educational center in the Eastern Caribbean.
- Culinary Diversity: Barbadian cuisine, or Bajan cuisine, is an eclectic mix of African, Portuguese, Indian, Irish, Creole, and British influences, famous for dishes like flying fish and cou-cou.
- Sporting Excellence: Barbados is passionate about sports, particularly cricket, with the island producing some of the world’s leading cricketers, including Sir Garfield Sobers.
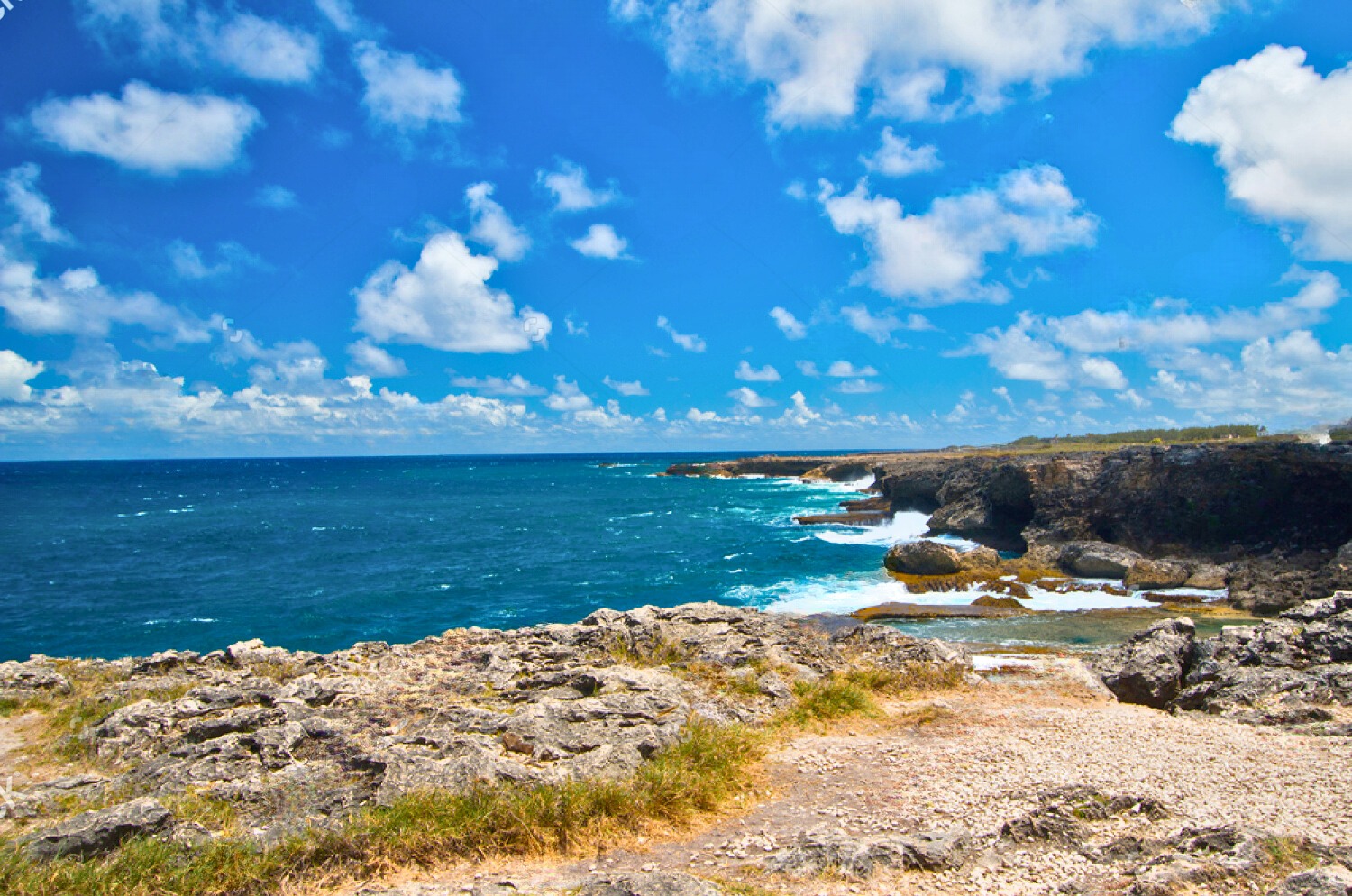
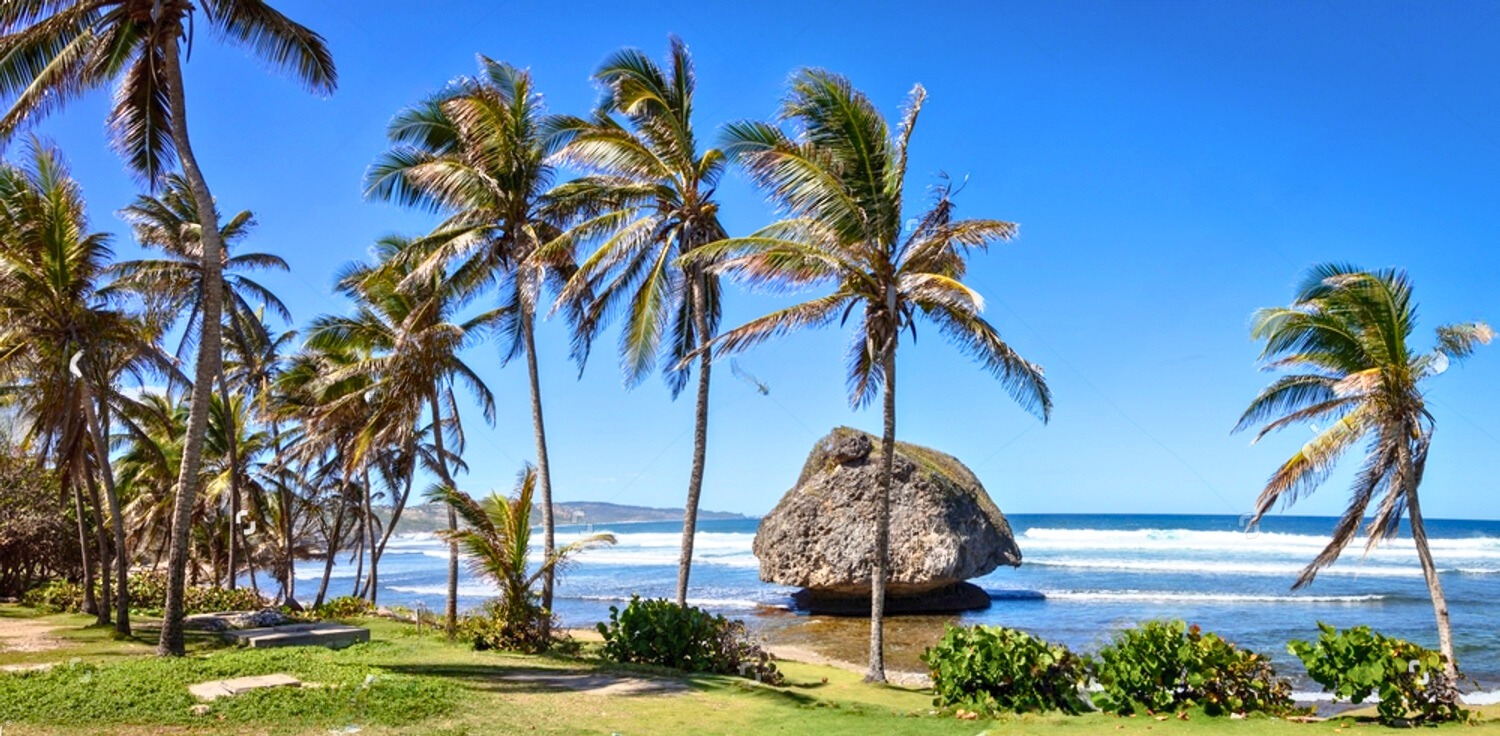
Places To Visit in Barbados
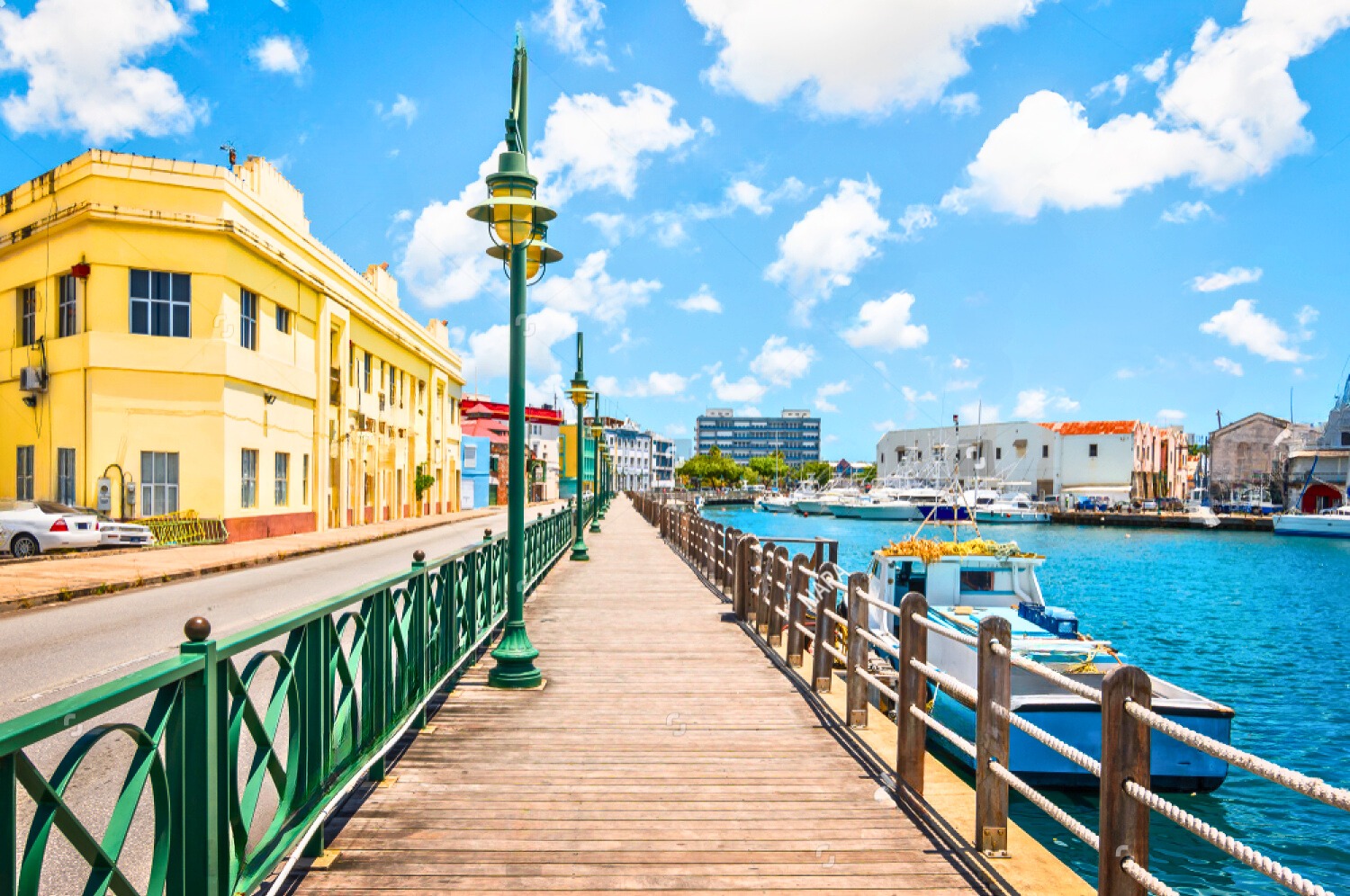
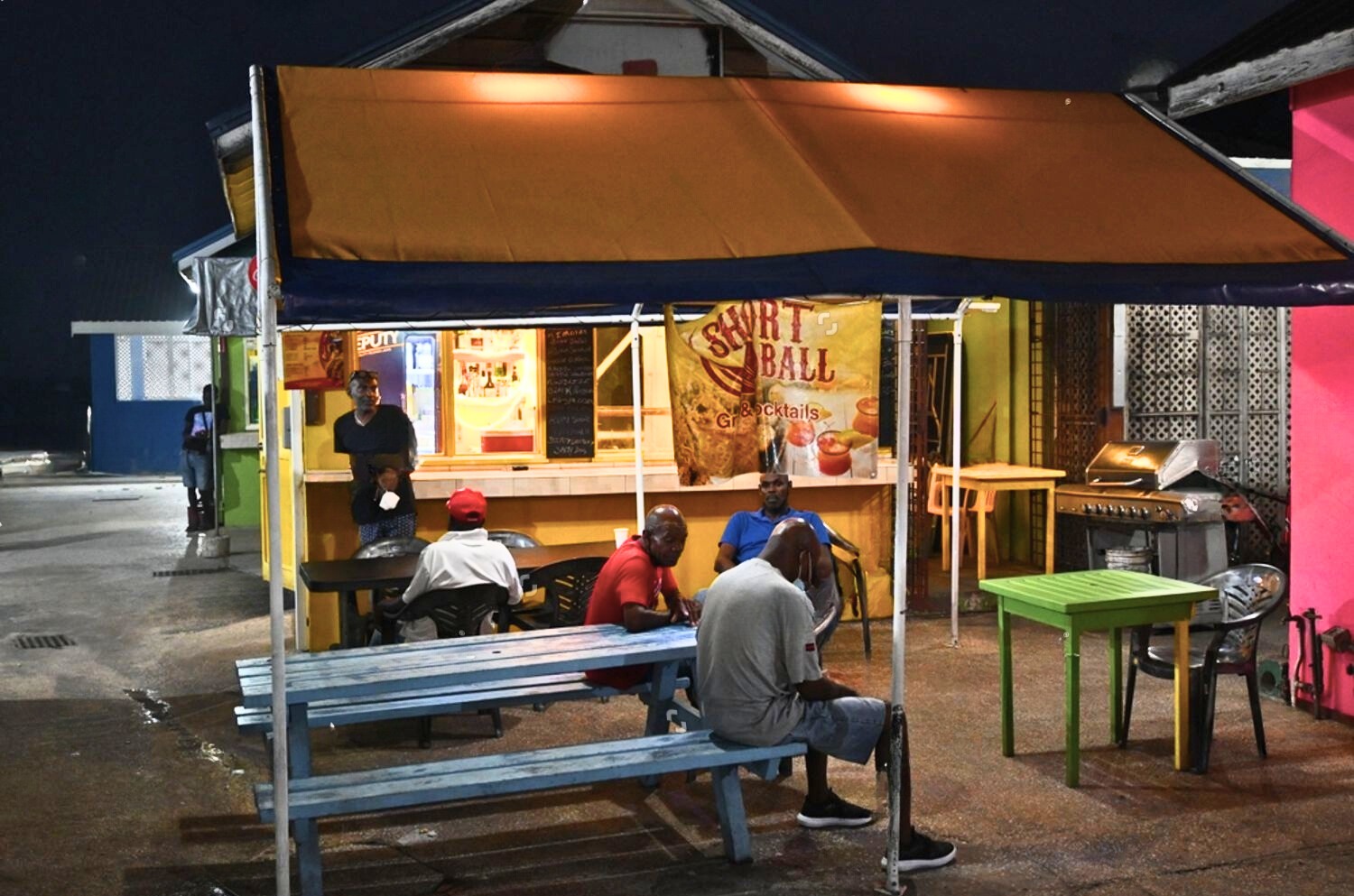
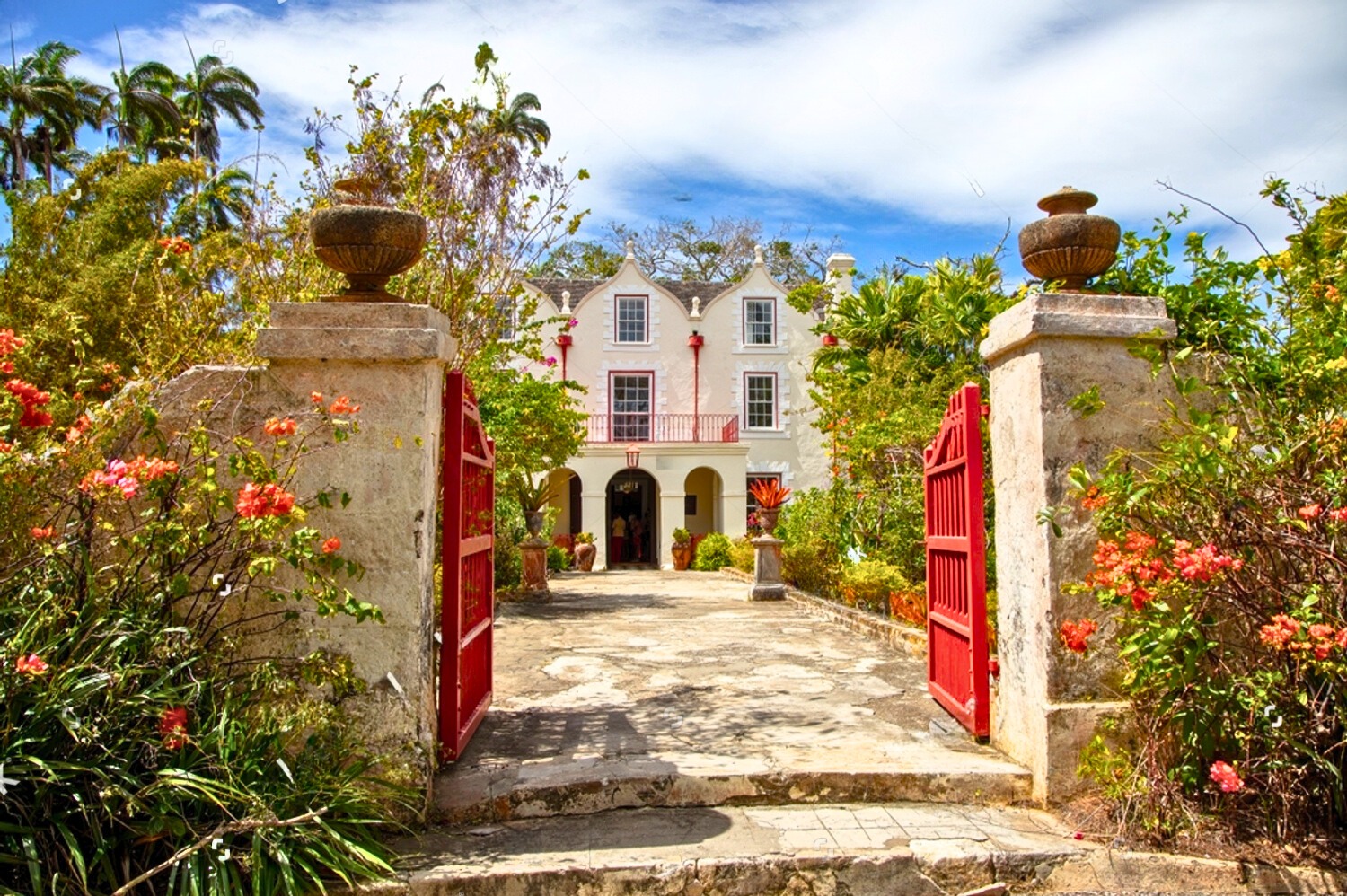
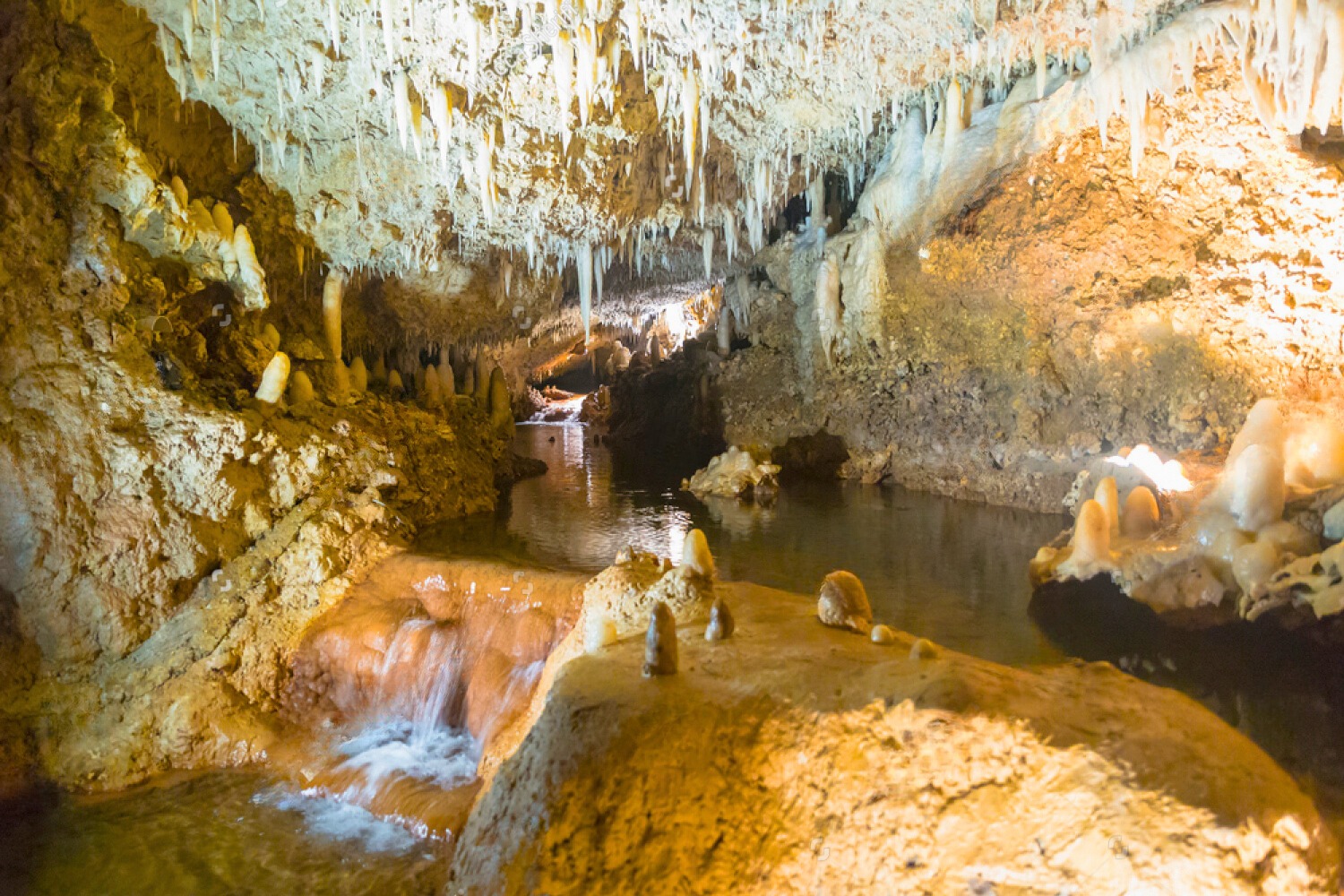






Events
Rhythms of Barbados
Barbados, a gem of the Caribbean, is steeped in rich history and vibrant cultural expressions, reflecting a blend of African, British, and West Indian influences. This island nation celebrates its diverse heritage through an array of festivals, music, and dance, making it a unique cultural destination.
- Barbados Sailing Week (January): Kicks off the sailing season with competitive races and vibrant shore-side activities.
- Holetown Festival (February): Celebrates the island’s heritage with music, dance, and parades marking the first settlement.
- Bridgetown International Arts Festival (March): Brings together artists from around the world in a multicultural celebration of the arts.
- Oistins Fish Festival (April): Honors local fishermen with fish-cooking contests and lively entertainment.
- Reggae Festival (April): Showcases top reggae talent from around the world in a series of concerts.
- Sir Garfield Sobers Golf Tournament (May): Hosts golfers from across the globe in a competitive tournament named after the cricket legend.
- Crop Over Festival (July-August): Marks the end of the sugar cane season with music, dance, and the colorful Grand Kadooment parade.
- Grand Kadooment Day (August): Features elaborate costumes and calypso bands in a vibrant street carnival.
- NIFCA Culinary Arts and Crafts Festival (November): Displays local arts and culinary skills in a celebration of Bajan culture.
- Barbados Independent Film Festival (January): Screens a diverse range of independent films from international filmmakers.
- Run Barbados Marathon Weekend (December): Offers a series of races along scenic routes, attracting runners worldwide.
- Barbados Food and Rum Festival (October): Highlights the island’s culinary arts and its rich history of rum-making.
Upcoming events in Barbados
Directory
Barbados Art Galleries Studios and Centers
Museums and Heritage
Richès Karayib has the great pleasure to introduce you to Akeem Chandler Prescod, known as StonedwithCupid, a multi-talented artist from Barbados.
The artist manipulates words with dexterity, he is creative, innovative and imaginative.
Let’s discover the artist and his talents.
ABOUT AKEEM @StonedwithCupid
StonedwithCupid is a spoken word artist, photographer, song-writer, and creative director from Barbados. His work is an experimental blend of Hip-Hop, Soul, Story-Telling, and Theatre, woven together in a neatly stitched poetic product.
This product has earned him: awards and prizes at NIFCA, nominations at the Gine On People’s Choice Awards where he was the first poet to be nominated in the Music Video of The Year Category, and even took him on a two-week performance tour in Bloemfontein, South Africa at the Vrystaat Kunstefees Festival.
His most recent accomplishment includes a feature in a regional Caribbean Showcase organised by Catapult and a second place finish in the Vybzing Youth Outreach Programme organised by the Caribbean Development Bank.
Off the stage, he possesses a Bachelor of Arts in Arts & Entertainment Management and has been the ambassador for NGOs such as Advocates against Domestic Violence and None in Three.
HOW ART AND CULTURE CAN BE CATALYSTS FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT WITHIN THE CARIBBEAN
Akeem Share with us his point of view.
Subtitles are available in french and spanish (settings)
KILLING ME SOFTLY - @stonedwithCupid & Casheda Dottin
Subtitles are available in french and spanish (settings)



































