In a significant boost for Caribbean cinemaThe 18th edition of the prestigious film laboratory, Nuevas Miradas, ended with eight Caribbean film projects receiving awards and support, thanks to the UNESCO-EU Transcultura program. This initiative, funded by the European Union, has played a key role in bringing Cuba, the Caribbean and the European Union closer together through culture and creativity.
The transcultura program: a catalyst for Caribbean cinema
The Transcultura program is a key element in the development of Caribbean cinemaoffering emerging filmmakers the opportunity to participate in major laboratories and events. This program is essential not only for developing local cinema, but also for connecting Caribbean countries, as they share similar histories and contexts.
Nuevas Miradas: a platform for young filmmakers
Organized by the Production Chair of the International Film and Television School in San Antonio de los Baños, Nuevas Miradas is one of the oldest and most prestigious laboratories in Latin America and the Caribbean. The event takes advantage of the presence of film industry representatives at the Havana International Film Festival to connect them with emerging filmmakers from the region, thus supporting the diversity of voices and stories in the
Caribbean cinema.



Award-winning projects: an overview of Caribbean storytelling
1. Escúchame – a documentary by Kevin Argudin (Cuba)
Escúchamedirected by Cuban filmmaker Kevin Argudin, is a documentary that explores the lives of individuals in Cuba, highlighting their struggles, hopes and daily realities. The project received direct access to the DocMx festival and support from Zafiro Cinema, recognizing its artistic quality and potential on the international scene, and contributing to the development of the Cuban film industry. Caribbean cinema.
2. El amor en tiempo de Bacanerías (Love in the Time of Bacanerías) – By Iván de Lara and Cristian Mujica (Dominican Republic)
Directed by Iván de Lara and produced by Cristian Mujica, El amor en tiempo de Bacanerías is a film that explores the complexities of love and relationships in the context of traditional Dominican festivals. The project received an invitation to the Cali Film Festival’s Producers and Film Projects Fair in Colombia, and an audience design consultation from the World Cinema Fund, reinforcing the project’s potential in the Dominican Republic. Caribbean cinema.
3. Non, je n’ai pas trouvé l’Eldorado – By Séphora Monteau and Wendy Desert (Haiti)
This Haitian film, directed by Séphora Monteau and produced by Wendy Desert, entitled No, I haven’t found El Doradois a poignant exploration of the quest for a better life and the disappointments that often follow. The project received coaching from Fonds Suisse Sud Est and advice on production and financing strategies from French documentary filmmaker Tancrède Ramonet, supporting the development of the Caribbean cinema.
4. La Isla de los Cangrejos (Island of the Crabs) – By Juan Carlos Guzmán and María José Martínez (Dominican Republic)
La Isla de los Cangrejosdirected by Juan Carlos Guzmán and produced by María José Martínez, is a fiction film that tells the story of a small island community struggling against environmental change and the impact of tourism. The project received script development support and was recognized for its unique storytelling, enriching the Caribbean cinema.
5. El Último Baile (The Last Dance) – By Carlos Pérez and Ana García (Cuba)
Directed by Carlos Pérez and produced by Ana García, El Último Baile is a documentary that captures the final days of a traditional dance troupe in Cuba. The project received funding for post-production and has been praised for its emotional depth and cultural significance, contributing to the richness of the Caribbean cinema.
6. La Lluvia de los Dioses (Rain of the Gods) – By David Fernández and Yamilé Alfonso (Guyana)
La Lluvia de los Diosesdirected by David Fernández and produced by Yamilé Alfonso, is a fiction film that combines mythology and reality in a Guyanese village. The project received a location scouting and pre-production grant, highlighting its innovative storytelling and enriching the Caribbean cinema.
7. El Silencio de las Olas (The Silence of the Waves) – By Rafael Ramírez and Lucía Hernández (Saint Kitts and Nevis)
Directed by Rafael Ramírez and produced by Lucía Hernández, El Silencio de las Olas is a documentary that explores the lives of fishermen in St. Kitts and Nevis, focusing on the challenges they face and their connection to the sea. The project received sound design support and was recognized for its cinematic beauty, contributing to the diversity of the Caribbean cinema.
8. La Casa de los Abuelos (The House of the Grandparents) – By José Luis Morales and Elena Rodríguez (Dominican Republic)
La Casa de los Abuelosdirected by José Luis Morales and produced by Elena Rodríguez, is a fiction film that tells the story of a family reunion in a traditional Dominican home. The project received funding for editing and was praised for its family-centric storytelling, enriching the Caribbean cinema.
Professionalizing young filmmakers
The Nuevas Miradas event not only contributes to the advancement of projects, but also serves as a platform to boost the cinematic careers of participants, in line with the objectives of the Transcultura program, which aims to support the diversity of voices and stories in Caribbean cinema.
Impact on the Caribbean film industry
Spaces like Nuevas Miradas are essential for presenting and internationalizing projects in their early stages of development. According to Yamila Marrero, General Coordinator of Nuevas Miradas, “A program like Transcultura, which enables emerging filmmakers to take part in major laboratories and events like Nuevas Miradas, is essential for developing our industry. Caribbean cinemabut also to connect with other Caribbean countries, as we share similar histories and contexts”.
Wendy Desert, Haitian director and producer, emphasized that “the event not only contributes to the advancement of projects, but also serves as a platform to boost the cinematographic careers of participants, in line with the objectives of the Transcultura program”.
The UNESCO-EU Transcultura programme has once again demonstrated its commitment to fostering the growth and international recognition of Caribbean cinema. En soutenant ces huit projets de film, le programme garantit que les histoires et les perspectives uniques de la région des Caraïbes soient entendues sur la scène mondiale. Alors que l’industrie cinématographique caribéenne continue d’évoluer, des initiatives comme Nuevas Miradas et le programme Transcultura restent cruciales pour nourrir les talents et promouvoir la diversité culturelle du Caribbean cinema.
La Dominican Republic is a must-see destination in the Caribbean, attracting millions of visitors every year. The country recently reached a remarkable milestone with the arrival of its 11 millionth visitor, underlining the meteoric rise of its tourism sector. This article delves into the heart of this phenomenon, exploring the reasons behind the tourism success of this beautiful island nation.
Historic staking
The 11 millionth visitor was enthusiastically welcomed at Punta Cana International Airport. Canadian Bruce Pirt and his family had the honor of symbolizing this achievement. The Minister of Tourism, David Collado, hailed this milestone, saying that “surpassing the 11 million visitor barrier is a historic achievement that consolidates the Dominican Republic as the region’s tourism leader”.
This impressive figure is not just a statistic; it represents 949,000 direct and indirect jobs and contributes $26 billion to the national economy. The Dominican Republic also generated 130 billion Dominican pesos in tax revenues, demonstrating the significant impact of tourism on the country’s economic growth.

Assets of the Dominican Republic
Natural beauty
The Dominican Republic boasts breathtaking scenery, from white sandy beaches to verdant mountains. The beaches of Punta Cana, Samaná and Puerto Plata attract sun-seekers and water-lovers alike. The crystal-clear waters are perfect for diving and snorkeling, while the mountains offer opportunities for hiking and exploring.
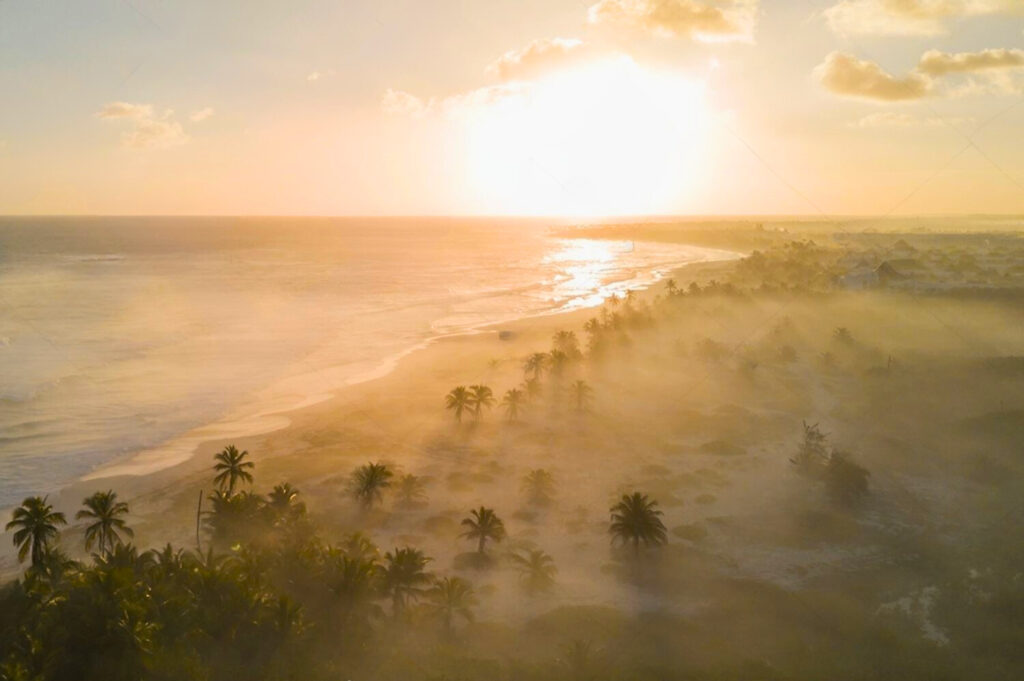
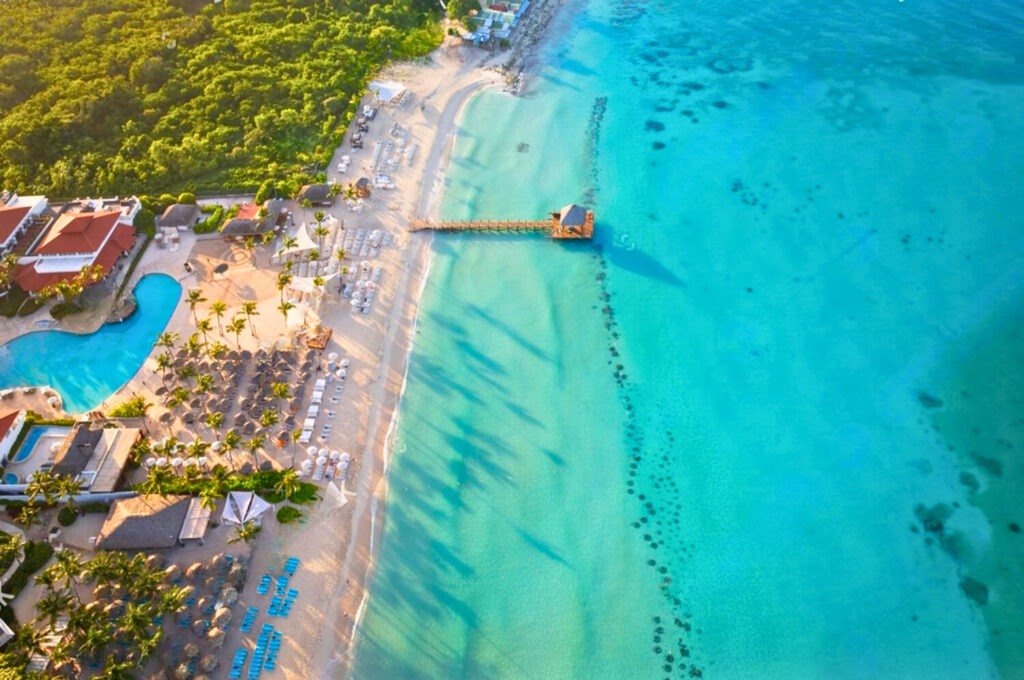
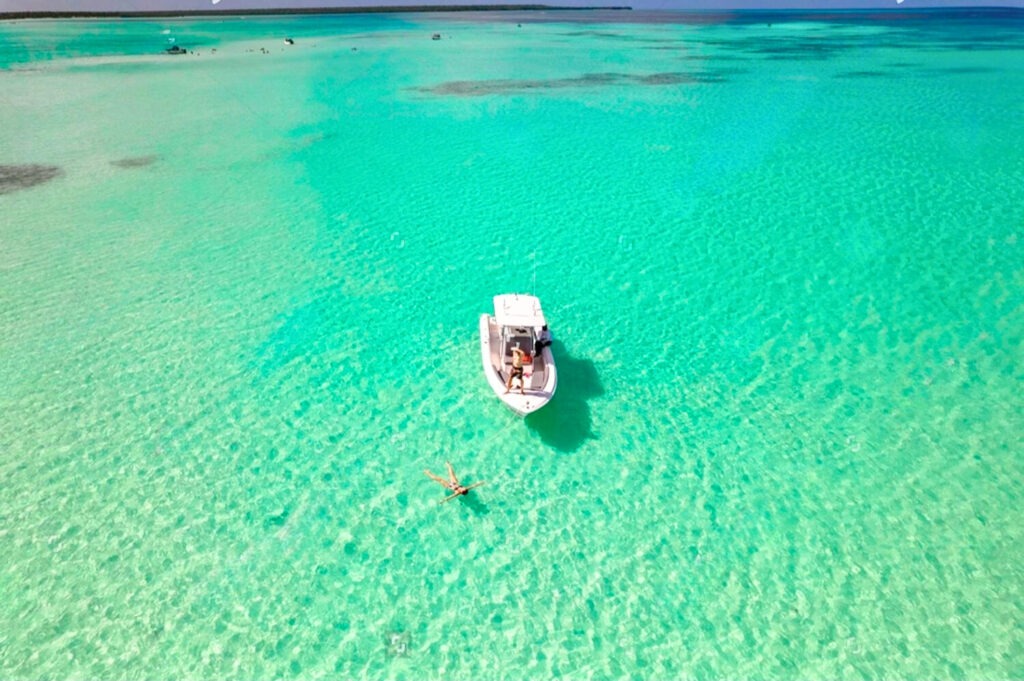
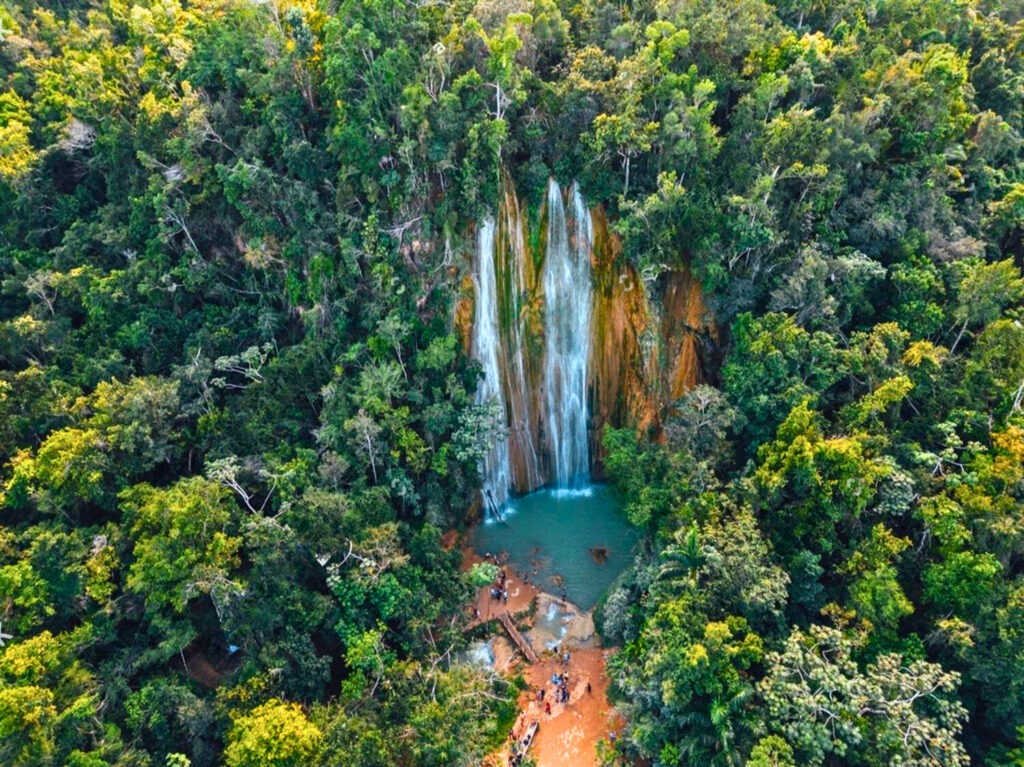
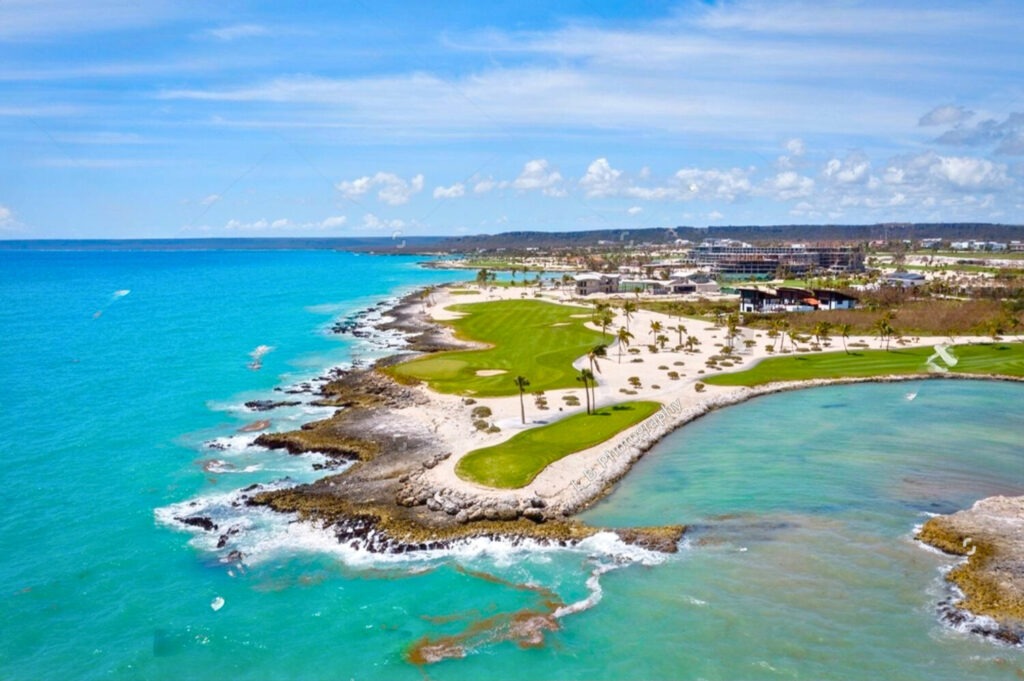
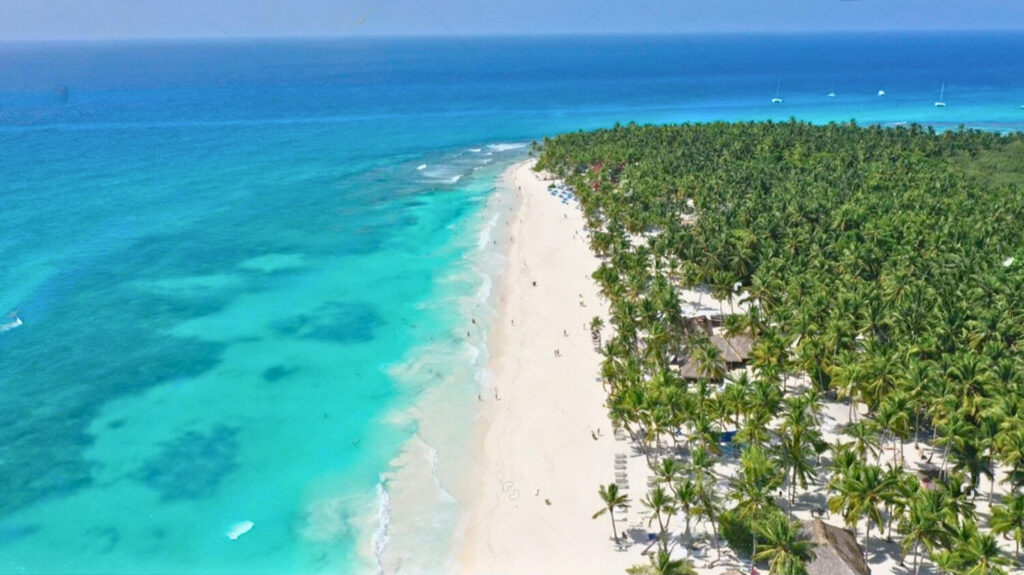






Rich culture
Dominican culture is a fascinating blend of African, Spanish and Taino influences. This diversity is reflected in its music, dance and gastronomy. Cultural festivals such as Carnival attract tourists who wish to immerse themselves in this rich tradition. Typical dishes, such as mangu and sancocho, seduce visitors’ palates.
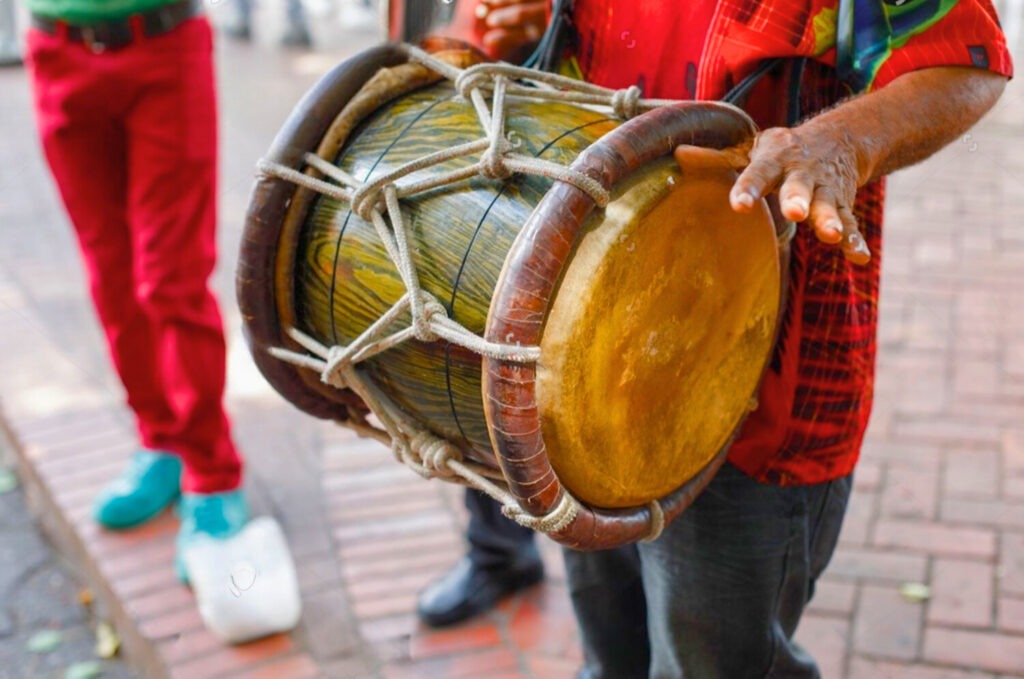
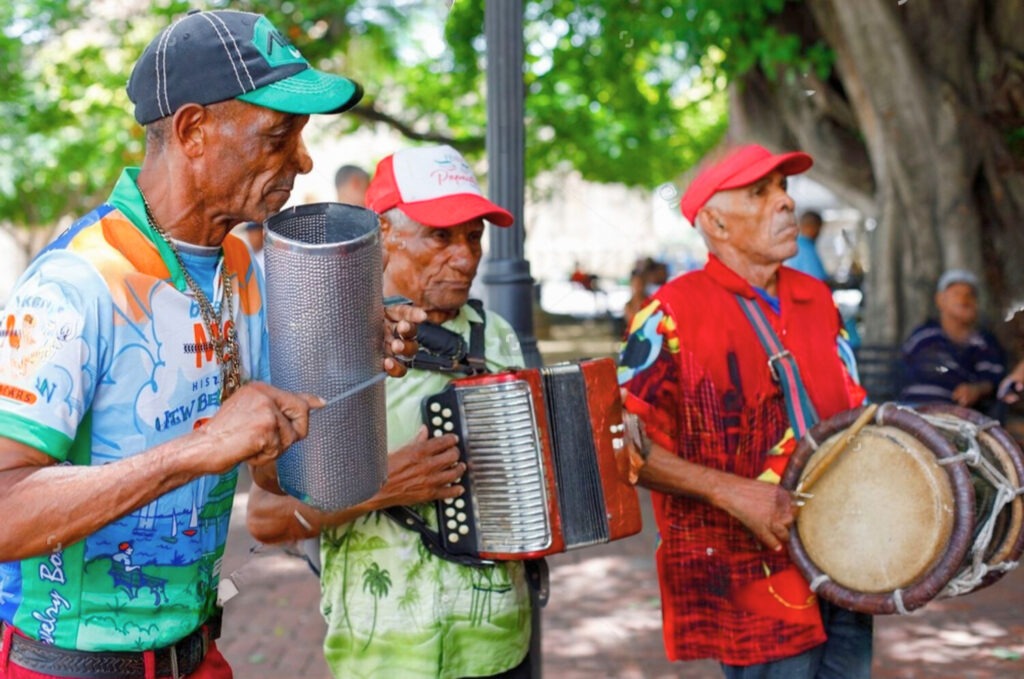


Quality accommodation
The Dominican Republic offers a diverse range of accommodation, from luxury resorts to small local inns. Major hotel chains are investing heavily in the country, guaranteeing quality service and modern facilities. This not only attracts tourists, but also boosts the local economy.

Diversified activities
Tourist activities in the Dominican Republic are varied and suitable for all ages. From boat trips to tours of coffee plantations, there’s something for everyone. Golf enthusiasts can enjoy world-class courses, while history buffs can explore the historic sites of Santo Domingo, the first city of the New World.
Economic impact of tourism
Tourism plays a key role in the Dominican economy. With 949,000 jobs linked to the sector, it is a driving force behind local employment. The income generated by tourism also helps to finance infrastructure, schools and hospitals, improving the quality of life for local residents.
Minister Collado stressed that this growth was the result of a collective effort between the public and private sectors. An effective marketing strategy has positioned the Dominican Republic as a destination of choice on the world stage.
A promising future for tourism
The Minister also expressed confidence in the future of tourism in the Dominican Republic. With infrastructure expansion projects and initiatives to promote the country internationally, the outlook is bright. Ongoing efforts to improve the visitor experience will ensure that the country remains a top destination.
The Dominican Republic is much more than just a tourist destination. It’s a place where natural beauty, vibrant culture and hospitality come together to create an unforgettable experience. With the welcome of its 11 millionth visitor, the country reinforces its position as a leader in the tourism sector. As visitors, we have the chance to discover this Caribbean wonderland, while contributing to the prosperity of its people.
Royal Caribbeana major player in the cruise industry, joins forces with the Caribbean Tourism Organization (CTO) to promote the sustainable growth of tourism in this paradise region. This month, a landmark event took place in Miami, the Caribbean Weekend, bringing together tourism ministers, executives and other key players to discuss the opportunities and challenges facing the sector.
An iconic tourism summit
The event, entitled “Envisioning Caribbean Tourism: An Iconic Summit”, was held on board Royal Caribbean‘s latest ship, the icon of the Seas. The meeting initiated vital discussions on job creation, sustainability and community engagement. Michael Bayley, President and CEO of Royal Caribbean, opened the proceedings, emphasizing the importance of the cruise industry to the Caribbean economy.
” The Caribbean is the soul of Royal Caribbean. Around 60% of our business comes from this region,” he said, emphasizing the deep ties between the company and the islands.
Royal Caribbean's commitment to sustainability
Sustainability is a central theme of this initiative. Bayley reaffirmed Royal Caribbean’s commitment to reducing its ecological footprint. Among the initiatives presented was the use of biofuels and liquefied natural gas (LNG) to power its ships. This demonstrates a commitment to meeting environmental challenges while continuing to support the local economy.
Ian Gooding-Edghill, Chairman of the CTO and Barbados’ Minister of Tourism and International Transport, also stressed the importance of cross-sector collaboration in achieving these goals. “We need to work together to reinvent the future of tourism in the Caribbean,” he said.

Employment opportunities and local sourcing
Royal Caribbean is also committed to creating employment opportunities for the people of the Caribbean. Bayley has highlighted the need to improve supply chain systems to support local producers. Working hand-in-hand with local ministries, the company aims to develop cooperatives that would facilitate the supply of fresh produce for its ships.
He also mentioned the American Caribbean Maritime Foundation’s cadet program, which enables talented young people to train and take part in the maritime industry. The story of a female officer from the Bahamas, who sailed aboard the Icon of the Seas, was particularly inspiring for participants.
The importance of partnerships
The summit highlighted the vital role of partnerships in transforming the tourism industry. Dona Regis-Prosper, Secretary General of the CTO, expressed her gratitude to Royal Caribbean for its ongoing commitment. She said, “This iconic summit underscores the power of partnerships and collaboration. We need to reimagine our approach to tourism development.”
Royal Caribbean is also committed to strengthening exchanges and communication between the industry’s various stakeholders. This includes a better understanding of the needs and challenges of Caribbean communities, to ensure that tourism development benefits all.
Royal Caribbean's vision for the future
As Royal Caribbean prepares to launch its next ship, Star of the Sea, Bayley reassured attendees that the Caribbean will continue to be at the heart of its operations. The company is committed to investing in the region, creating a future where sustainable growth and the economic well-being of the Caribbean are paramount.
Supporting sustainability initiatives and promoting local culture are key elements of this vision. This involves not only financial investment, but also a long-term commitment to local communities.
A promising future for tourism
The Miami meeting was a pivotal moment for the Caribbean tourism sector. Thanks to the collaboration between Royal Caribbean and the CTO, new opportunities for sustainable growth are on the horizon. The discussions held at the summit should serve as a springboard for future initiatives, aimed at ensuring that tourism in the Caribbean is both economically viable and environmentally friendly.
By further integrating local stakeholders into the development process and adopting sustainable practices, Royal Caribbean is proving that it is possible to combine pleasure and responsibility. The future of tourism in the Caribbean looks bright, and with a strong commitment and solid partnerships, it’s likely that this region will continue to shine on the world tourism stage.
Christmas in the Caribbean is a unique time of celebration, filled with colorful traditions and tasty dishes. The Caribbean islands are known for their festive atmosphere, and cuisine is at the heart of these festivities. The magic of Christmas in this region is palpable, with bright decorations, joyful carols and, above all, dishes that awaken the senses. In this article, we’ll explore four iconic recipes that make Christmas unforgettable: lambi or grilled fish with sosé, Great cake, Christmas ham tuiles and nwel ham.
1. Lambi or grilled fish with sosé
Ingredients
- Lambi or fish of your choice
- Local spices
- Tomatoes
- Peppers
- Onions
Preparation
- Cleaning the lambi: If you use lambi, clean it thoroughly to remove all sand and impurities.
- Marinade: Marinate lambi or fish with local spices to enhance flavours.
- Grilling: Grill on the barbecue or in a frying pan, taking care to cook thoroughly.
- To prepare the sauce: In a saucepan, sauté the onions, tomatoes and peppers with the spices, then add water and simmer until cooked through.
This tasty dish, often served with rice or vegetables, is a staple of Christmas tables in the Caribbean, symbolizing the richness of local maritime resources.

2. Great cake
Ingredients
- 1/2 cup dried fruit
- 113.4 g nuts (almonds or peanuts)
- 227 g sugar
- 227 g flour
- 6 eggs
- Spices (cinnamon, nutmeg, cloves)
Preparation
- Fruit preparation: Wash and dry the fruit, then soak it in alcohol for several months for a rich taste.
- Caramel: Melt the sugar to a caramel-like consistency. Add it to the mixture.
- Mixing the ingredients: In a large bowl, mix the sugar and margarine, then add the eggs one by one.
- Adding fruit and nuts: Add fruit and nuts to the dough.
- Baking: Pour into a baking tin and bake at 300°F for about 2 hours 30 minutes.
The large cake, often rich in flavor and alcohol, is a tradition that brings warmth and conviviality to festivities. It is often served at family gatherings and is a symbol of Caribbean hospitality.

3. Nwel ham
Ingredients
- 1 Christmas ham
- Red sugar
- Spicy sauce (cinnamon, nutmeg, etc.)
- Pineapple
Preparation
- Defrosting: Make sure the ham is completely defrosted before starting to prepare it.
- Caramel: Melt the sugar in a pan until you obtain a golden caramel.
- Brushing: Brush the ham with the caramel and add the spicy sauce.
- Baking: Bake at 180°C for 30 to 40 minutes, basting regularly to keep the ham juicy.
Jamon nwel is usually the main course at Christmas meals, representing celebration and family unity. It is usually served with side dishes such as mashed potatoes or roasted vegetables.

4. Christmas ham tiles
Ingredients
- Brick pastry
- Christmas ham
- Unsalted butter, melted
Preparation
- Dehydrating ham: Dehydrate the ham and crumble it into fine crumbs to obtain the perfect texture.
- To prepare the brick pastry sheets: Place the ham crumbs in brick pastry sheets, previously brushed with melted butter.
- Cooking: Brown the tiles in a non-stick frying pan or in the oven until crisp and golden.
These crunchy tuiles are the perfect start to a festive meal, adding a crunchy touch to any celebration. Served with a spicy sauce or fruit jam, they’re sure to delight your guests.

The flavors of Christmas in the Caribbean are a sensory experience that delights the taste buds. Whether it’s crispy ham tuiles, savory lambi, rich grand gâteau or fragrant nwel ham, each dish tells a story of tradition and conviviality. Not only are these recipes delicious, they also bring invaluable warmth to family Christmas gatherings. Each of these culinary creations evokes memories and shared moments, making every Christmas even more memorable.
Chukka Caribbean Adventures, with its stunning white sand beaches, turquoise waters, and rich biodiversity, represents a dream destination for many travelers. At the heart of this enchanting region, one company stands out for its commitment to sustainable tourism and customer experience: Chukka Caribbean Adventures.
Recently, Chukka was honored as the “World’s Leading Destination Experiences 2024” at the 31st World Travel Awards, celebrating its role as a leader in the adventure tourism industry. This article explores the impact of Chukka Caribbean Adventures on the tourism sector, its innovative approach, and the reasons it has become a benchmark in tourist experiences.

A Commitment to Sustainable Tourism
Chukka Caribbean Adventures was founded to provide authentic experiences while preserving the environment and supporting local communities. The company is devoted to protecting the fragile ecosystems of the Caribbean by integrating sustainable practices into every aspect of its operations. This includes using eco-friendly materials, reducing waste, and raising customer awareness about the importance of conservation.
Marc Melville, the CEO of Chukka, stated: “Our mission is to create extraordinary experiences that reflect the beauty and culture of the Caribbean while respecting our environment.” This commitment to sustainability has allowed Chukka to stand out in an increasingly competitive sector, where travelers seek options that positively impact the communities they visit.
Diverse and Immersive Experiences
Chukka Caribbean Adventures offers a wide range of activities that go beyond simple tourist excursions. Whether outdoor adventures, cultural immersions, or adrenaline-pumping activities, each experience is designed to foster a deep connection with the environment and local communities.
Eco-Adventures
The eco-adventures offered by Chukka allow travelers to discover the unique biodiversity of the Caribbean. From kayaking through mangroves to hiking in tropical forests, each activity is guided by experts who share their knowledge of local wildlife and flora. These educational experiences enable visitors to understand the importance of preserving these ecosystems and encourage responsible tourism practices.
Cultural Immersions
The cultural aspect of Chukka’s offerings is equally enriching. Visitors can participate in artisanal workshops, explore local cuisine, or attend traditional music and dance performances. These immersions not only entertain; they also support local artisans and artists, creating a virtuous cycle where tourism directly benefits communities.
Thrilling Activities
For thrill-seekers, Chukka Caribbean Adventures offers exhilarating activities such as zip-lining, rafting, and scuba diving. These experiences are designed to provide an adrenaline rush while adhering to the strictest safety standards. By integrating these activities into a sustainable framework, Chukka ensures that visitors can enjoy adventure without compromising environmental integrity.
The Impact of the World Travel Awards
Receiving the title of “World’s Leading Destination Experiences 2024” at the World Travel Awards is a significant achievement for Chukka Caribbean Adventures. These awards, often compared to the “Oscars of Travel,” recognize leaders who innovate and drive excellence in the tourism sector. This distinction shines a light not only on the hard work of the Chukka team but also on the growing importance of sustainable tourism globally.
A Well-Deserved Recognition
This recognition crowns over 40 years of experience in the adventure tourism sector. Since its inception in 1983, Chukka has adapted to market changes and consumer expectations while remaining true to its core values. The company’s ability to innovate while preserving its commitment to sustainability is what places it at the forefront of the industry.
In summary, Chukka Caribbean Adventures is more than just a tourism company; it is a model of success in the field of sustainable tourism. Through its commitment to environmental protection and support for local communities, Chukka offers experiences that leave a positive footprint on travelers and the Caribbean region.
By winning the title of “World’s Leading Destination Experiences 2024,” Chukka confirms its status as a leader in the tourism industry and inspires other companies to follow its example.
For travelers seeking unique and responsible adventures, Chukka Caribbean Adventures represents an essential option. Whether you’re looking for cultural immersion, an escape into nature, or an adrenaline rush, Chukka invites you to discover the best of the Caribbean while respecting the environment and supporting local communities.
Our existence relies on the fundamental pillar of nutrition. It is much more than a biological necessity; it plays a crucial role in our physical health and overall well-being. Eating is not limited to the mere consumption of food; it reflects our culture, socio-economic background, and environment.
Today, Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet have become essential topics because our dietary choices can significantly influence our health. With public health concerns on the rise, understanding and adopting responsible eating habits has become crucial for living healthily.
Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet: Are They Achievable?
A Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet should ideally be a part of daily life in the Caribbean. However, many individuals face challenges that hinder their ability to eat healthily.
Reasons for Unhealthy Eating Habits
- Economic Constraints: Many families in the Caribbean encounter economic challenges, making it difficult to prioritize healthy foods. Processed and convenient foods, often cheaper and more accessible, have become the norm.
- Availability of Fresh Produce: In some areas, particularly those reliant on imports, fresh fruits and vegetables may not be easily available. This lack of accessibility can lead to a dependence on canned or packaged foods, which are less nutritious.
- Cultural Influences: While traditional Caribbean cuisine is rich in nutrients, globalization has introduced fast food and processed options that are frequently preferred for their convenience and taste. This shift can overshadow healthier food options from local gastronomy.
- Lack of Nutrition Education: There is often a lack of awareness regarding what constitutes a Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet. Educational initiatives focused on nutrition can help individuals make healthier choices and understand the importance of local ingredients.
What is Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet?
A Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet includes a variety of foods from all food groups at every meal, including proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. It is essential to understand that carbohydrates are not just the added sugars found in beverages but also come from sources like grains, fruits, and certain vegetables. A Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet incorporates these elements at each meal, ensuring a diverse intake of nutrients that reflect the vibrant culinary traditions of the Caribbean.
The Link Between Food self-sufficiency in the Caribbean and Healthy Eating
Food self-sufficiency is a crucial concept for the Caribbean region, where economic and environmental challenges directly influence the health of populations. The interconnection between food sovereignty and healthy eating deserves close examination, as it highlights the importance of consuming local foods and promoting sustainable food systems.
What is Food self-sufficiency ?
Food self-sufficiency refers to the ability of a community or country to produce enough food to meet its dietary needs. This involves not only agricultural production but also access to healthy, nutritious, and culturally appropriate foods. In the Caribbean islands, where food imports are common, strengthening food sovereignty can reduce dependence on imported food items and improve the nutritional quality of local diets.
Impact on Health
Increased food sovereignty allows communities to consume more fresh, seasonal, and locally grown foods, which are essential for healthy eating. Local products, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and fish, are often more nutritious than processed imported foods. By incorporating these foods into their daily diets, Caribbean residents can benefit from improved physical and mental health.
Cost Reduction and Sustainability
Consuming local foods can also help reduce food costs. Imported products are often more expensive due to transportation and storage costs, while locally grown foods are generally more affordable. By promoting food sovereignty, communities can develop sustainable food systems that support the local economy while ensuring access to healthy foods.
Valuing Traditional Agricultural Practices
Food sovereignty also encourages the appreciation of traditional agricultural practices, which are often adapted to the region’s environmental conditions. These practices may include growing local varieties of fruits and vegetables that are not only nutritious but also resistant to diseases and climate conditions. Reconnecting with these traditional methods strengthens not only food security but also local culture and identity.
The 50-25-25 Rule: A Strategy for Healthy Eating?
The well-known 50-25-25 rule suggests that a plate should consist of 50% vegetables, 25% proteins, and 25% carbohydrates. This rule serves as a general guideline for improving one’s plate and moving towards a Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet. The 50% of vegetables should include a variety of types, many of which are locally grown and reflect the rich agricultural heritage of the Caribbean.
For proteins, choices can range from fresh fish and plant-based options to meats sourced from sustainable practices. Carbohydrates should be rich sources, such as grains and fruits that are abundant in the region.
While this rule is beneficial, it is important to note that nutrition is highly individual. People with specific health conditions may need to tailor their diets accordingly, exploring local flavors and ingredients that resonate with their heritage.

The Role of Fats in a Healthy Diet
Some might wonder if the absence of fats in the 50-25-25 rule implies that fats should be eliminated from a Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet. This is not the case; fats are essential. Most foods naturally contain some fats. For instance, olives, avocados, and coconut are staples in Caribbean cuisine, providing healthy fats that enhance both flavor and nutrition. The focus should be on how foods are prepared and the quality of fats used in cooking, celebrating the culinary techniques that have been passed down through generations.
Benefits of Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet
A Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet form the foundation of well-being. Modern medicine emphasizes prevention over treatment. A healthy diet can help avoid certain conditions like diabetes and hypertension, which are prevalent in many communities. Moreover, good nutrition positively impacts mental health. People who eat well tend to concentrate better, feel more energized, sleep better, and integrate more smoothly into society. Embracing local cuisine not only promotes health but also fosters a sense of pride in cultural identity.
Correcting the Signs of Poor Nutrition
Is it easy to correct the signs of poor eating habits? While it may not be straightforward, visible changes can occur with dietary adjustments. For instance, many individuals may experience improvements in skin conditions simply by altering their diets. Simple changes, whether drastic or gradual, can lead to significant improvements in health, especially when incorporating local fruits and vegetables that are rich in nutrients.
Choosing the Right Foods for Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet
When selecting foods, there are two scenarios. One involves seeking professional guidance to assess and create a personalized nutrition plan based on individual needs. The other involves individuals making choices for themselves. In either case, incorporating a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables into every meal is key to achieving a Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet. It isn’t necessary to completely eliminate certain foods, but reducing industrial sugars is crucial for health while emphasizing the use of local ingredients.
The Impact of Restrictive Diets on Healthy Eating
In today’s world, many people embark on restrictive diets. Are these practices truly healthy in the long term? It’s important to clarify that the focus should be on eliminating industrial sugar and processed foods rather than following extreme diets. Each person’s needs are unique, and what works for one individual may not work for another.
The Importance of Hydration in Healthy Eating
Hydration is vital for a Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet. The body cannot function properly without adequate water intake. The minimum recommendation is about 2.5 liters of water per day, but this may vary based on activity levels. Proper hydration supports a Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet, as the body needs sufficient water to function effectively, particularly in tropical climates where hydration is essential.
Access to Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet
For those who believe that healthy eating is expensive, this misconception can often stem from seeking out exotic or imported foods. It is possible to maintain a Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet using locally available products. Embracing local produce can make healthy eating more accessible and affordable, allowing individuals to connect with their cultural roots while promoting sustainability.
In conclusion, it is essential to prioritize health rather than just focusing on weight. The journey towards better health starts with personal choices. It’s important not to wait until health issues arise before making dietary changes. With a commitment to a Healthy Eating and Balanced Diet, many health problems can be prevented.
Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean has become an essential aspect of the region’s development. With its rich cultural heritage, breathtaking natural landscapes, and unique traditions, the Caribbean attracts millions of visitors each year. The promotion of these cultural elements as tourist attractions is crucial for preserving local identity while meeting the needs of visitors. This article examines the challenges and opportunities associated with sustainable tourism in the Caribbean, emphasizing cultural heritage’s role in enhancing tourist experiences.
The Importance of Cultural Heritage in Tourism
Cultural heritage encompasses the traditions, customs, arts, and historical narratives that define a community. In the Caribbean, this heritage is diverse and multifaceted, reflecting the region’s complex history influenced by Indigenous peoples, European colonization, African cultures, and more. Tourists are drawn to the Caribbean not only for its stunning beaches but also for its vibrant cultures, making cultural heritage a significant driver of tourism.
By integrating cultural experiences into tourism offerings, destinations can attract visitors seeking authentic experiences. This approach not only enriches the tourist experience but also fosters a deeper appreciation for local cultures, leading to a more sustainable form of tourism.


Challenges of Sustainable Tourism
Pressure on Cultural Resources
The influx of tourists can lead to excessive exploitation of cultural resources, such as festivals, traditional events, and historical sites. This pressure can compromise the authenticity and longevity of local cultural practices. Destinations often face the dilemma of balancing tourism growth with the preservation of their unique cultural identities.
For instance, traditional festivals may be altered to cater to tourist expectations, potentially losing their original significance. This commercialization can lead to a superficial understanding of the culture, with visitors experiencing a version that is tailored for mass consumption rather than genuine engagement.
Erosion of Cultural Identity
Mass tourism can sometimes result in the commercialization of traditions, leading to a dilution of cultural identity. Local practices may be adapted to meet tourist expectations, creating a disconnect between genuine traditions and those presented to visitors. The risk of cultural appropriation also arises, where elements of local culture are taken out of context and used superficially by outsiders.
Moreover, younger generations may feel less inclined to engage with their heritage if they perceive it as something primarily for tourists. This generational shift can threaten the transmission of cultural knowledge and practices, jeopardizing the long-term sustainability of local traditions.
Infrastructure and Management
Many Caribbean destinations lack adequate infrastructure to manage the flow of tourists interested in culture. This can result in challenges related to site management, preservation of artifacts, and respect for traditional practices. Insufficient funding for the maintenance of cultural sites can lead to deterioration, further diminishing their appeal to tourists.
Effective management strategies are essential to ensure that cultural sites can accommodate visitors without compromising their integrity. This may involve training local guides, implementing visitor limits, and developing educational programs that emphasize the importance of conservation.
Vulnerability to Environmental Changes
Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, can destroy cultural and historical sites, jeopardizing the heritage that attracts tourists. The resilience of these sites is essential to ensure continued tourist appeal. Climate change poses a significant threat to the Caribbean, with rising sea levels and increased storm frequency impacting both the environment and cultural heritage.
Investments in disaster preparedness and recovery are crucial for safeguarding these sites. By building resilient infrastructures and promoting sustainable tourism in the Caribbean , destinations can better withstand environmental challenges.
Opportunities of Sustainable Tourism
Highlighting Local Traditions
Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean provides a platform to promote the arts, music, dance, and festivals that are central to Caribbean identity. Events such as Carnival in Trinidad and Tobago, Junkanoo in The Bahamas, and Reggae festivals in Jamaica showcase the vibrant cultural tapestry of the region. By integrating authentic cultural experiences into tourist offerings, visitors can discover the richness of the Caribbean while supporting local communities and patricipate to the sustainable tourism in the Caribbean.
Local artisans can also benefit from Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean. By encouraging the purchase of handmade crafts and artworks, tourism can contribute to preserving traditional skills and providing economic opportunities for local artists.
Education and Awareness
Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean offers an opportunity to raise visitor awareness about cultural and environmental issues. Guided tours, workshops, and cultural events help tourists develop a deeper understanding of local realities and the importance of heritage preservation. Educational initiatives can empower visitors to engage more meaningfully with the culture, fostering respect and appreciation.
For example, cultural immersion programs that involve community members can provide tourists with insights into daily life, traditions, and the challenges local communities face. This engagement can enhance the overall visitor experience, making it more impactful and memorable.
Community Economic Development
Focusing on culture as a tourist attraction allows local communities to benefit directly from the tourism economy. This encourages the creation of artisanal businesses, cultural tours, and services related to the arts, thus stimulating local economic development. Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean can empower communities by providing job opportunities and fostering entrepreneurship.
Moreover, when tourists spend money on local products and services, the economic benefits circulate within the community, contributing to its overall well-being. This model promotes a more equitable distribution of tourism revenues, reducing reliance on external entities.
Sustainable Partnerships
Developing partnerships among governments, cultural organizations, and the private sector is crucial for promoting Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean. These collaborations can support initiatives that preserve cultural heritage while providing enriching experiences for visitors. By working together, stakeholders can create a comprehensive approach to Sustainable tourism in the Caribbean that addresses environmental, social, and economic dimensions.
For instance, partnerships can facilitate joint marketing efforts that highlight cultural events, promoting them to a broader audience. Collaborative projects can also enhance the infrastructure necessary for managing tourism sustainably, ensuring that cultural sites are well-maintained and accessible.
To conclude, sustainable tourism in the Caribbean presents both challenges and opportunities, particularly in terms of valuing culture as a tourist attraction. By adopting environmentally respectful practices and highlighting local traditions, the region can preserve its unique heritage while offering memorable experiences to visitors. A collective commitment from tourism stakeholders, local communities, and governments is essential to create a development model that benefits all, celebrating the diversity and authenticity of the Greater Caribbean.
The path forward involves recognizing the intrinsic value of culture and heritage in tourism, fostering a sense of pride among local communities, and ensuring that tourism serves as a force for positive change. By embracing sustainable tourism practices, the Caribbean can continue to thrive as a premier destination while honoring its rich cultural legacy.
Celebrating the Caribbean’s Cultural Diversity
Between 2016 and 2019, UNESCO continued to recognize the Caribbean’s rich intangible cultural heritage, celebrating traditions that showcase the region’s diversity and vibrant history. These recognitions by UNESCO reveal the deep cultural practices and customs that have survived generations, connecting the past with the present. This article focuses on the elements honored during this period, highlighting their significance to the Caribbean identity.
2016
-
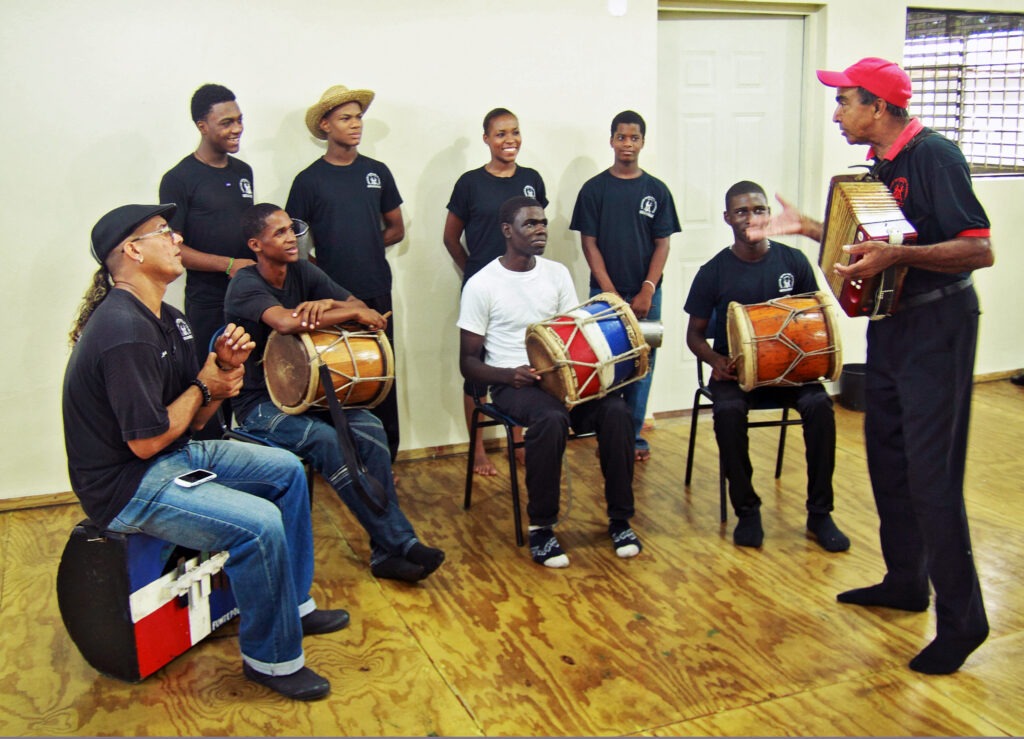
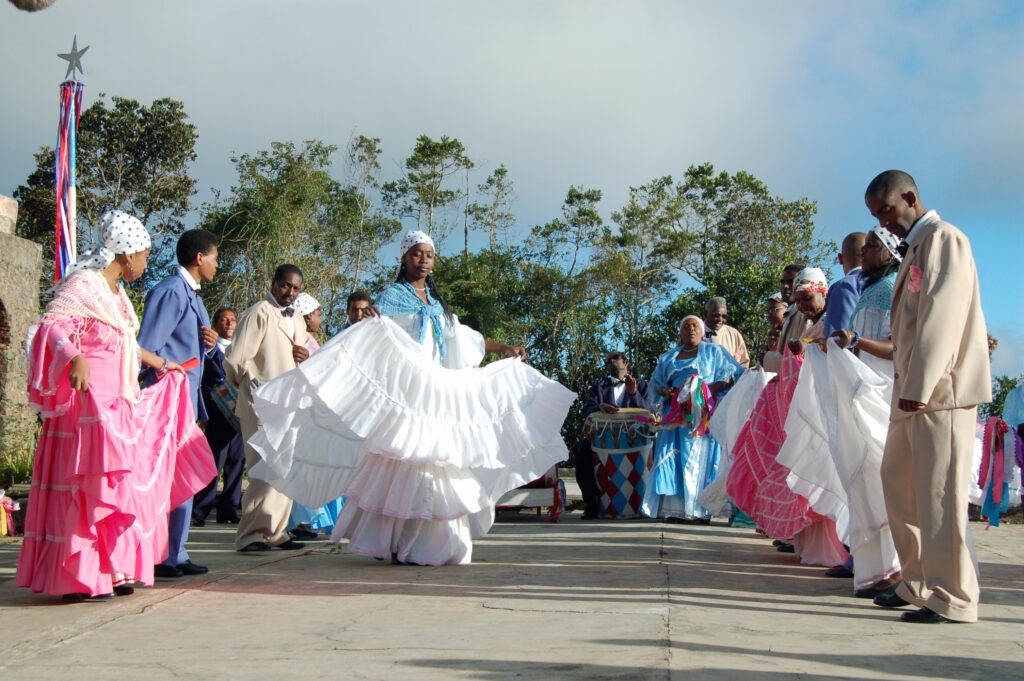
Dominican Republic: Music and Dance of Merengue
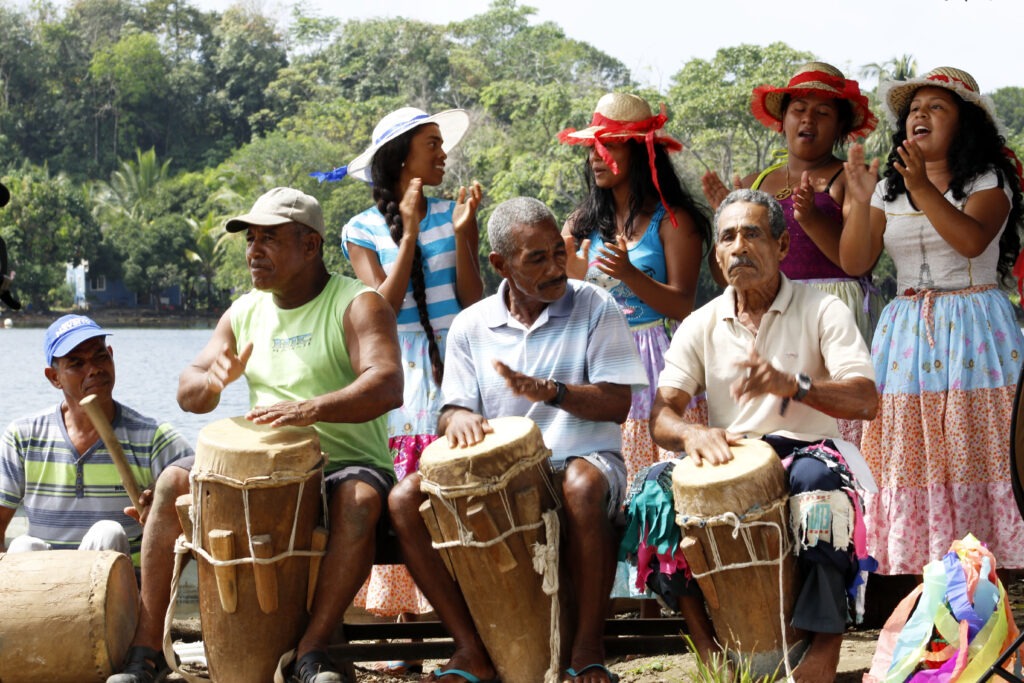
For UNESCO Merengue is not just a genre of music in the Dominican Republic but a national symbol. Its fast rhythms and lively dance steps are part of every major celebration. The music blends European and African influences, representing a fusion that is emblematic of the island’s history and cultural makeup. -
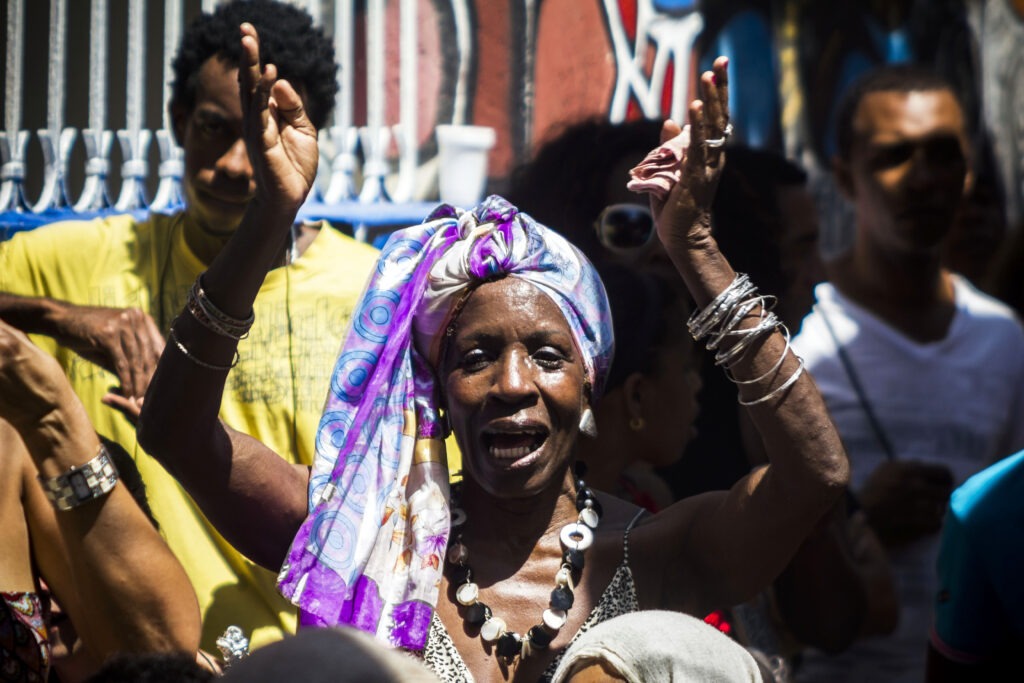
Cuba: Rumba
Rumba is a joyous celebration of Cuban identity through a fusion of African rhythms and Spanish melodies. It is more than a musical genre—rumba incorporates dance, percussion, and vocals, creating an art form that fosters community, expression, and connection with heritage. -
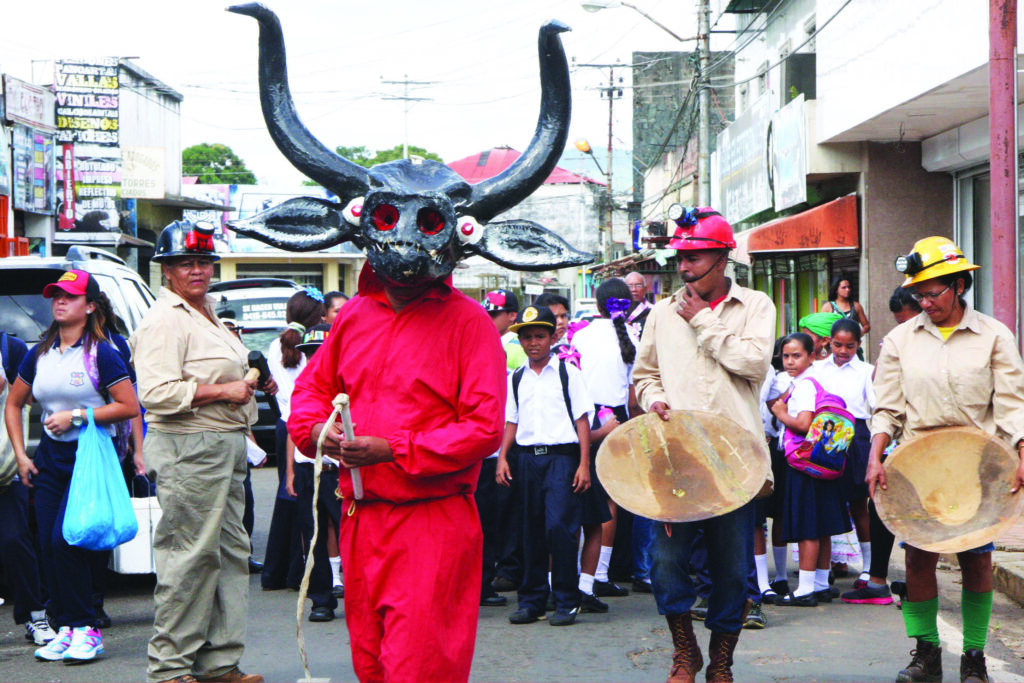
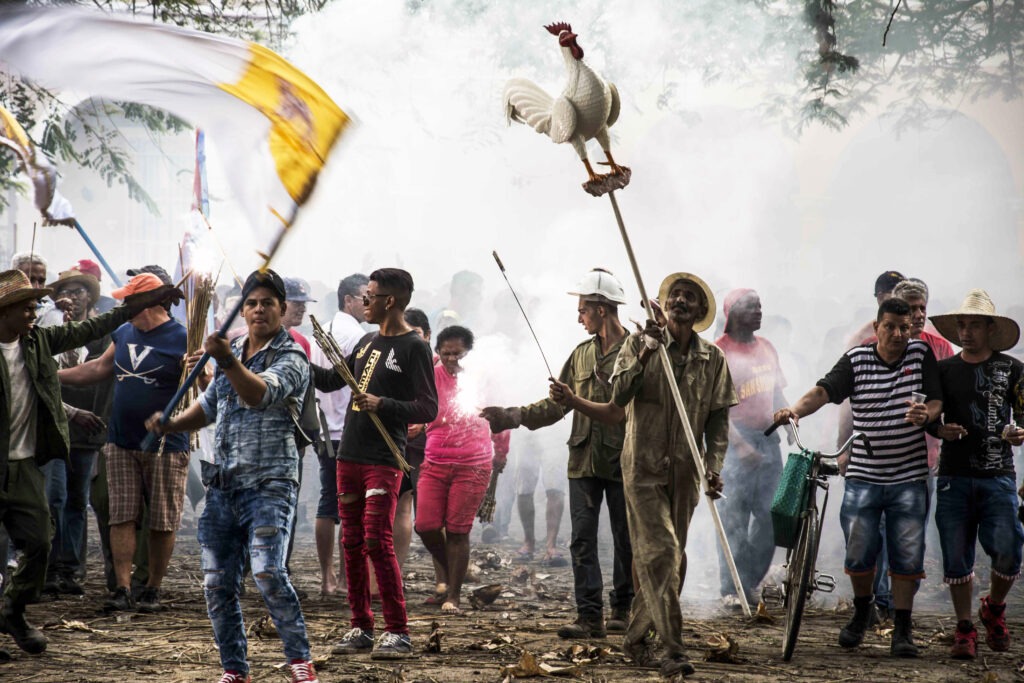
Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of): Carnival of El Callao
El Callao Carnival is a colorful and vibrant cultural event that dates back to the 19th century. It celebrates African, indigenous, and Caribbean roots through parades, masquerades, and traditional music. The carnival symbolizes unity and cultural resilience in the face of hardship, making it a significant event for Venezuelans. -
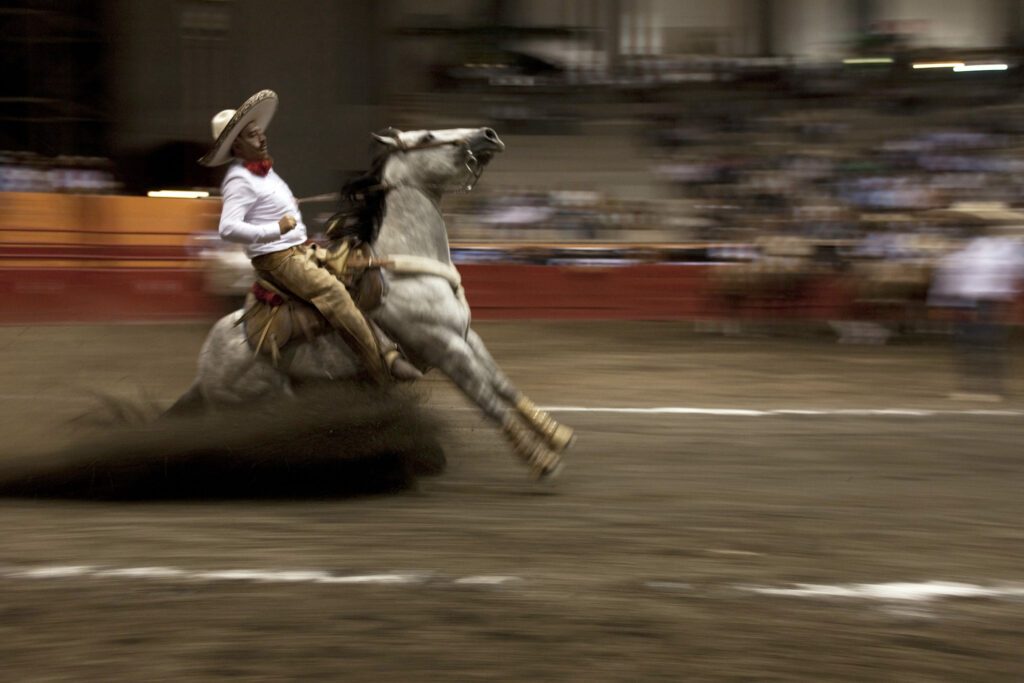
Mexico: La Charrería, Equestrian Tradition
La Charrería is a traditional equestrian practice among cattle-raising communities in Mexico that combines cultural heritage and competitive sport, showcasing skillful performances while promoting important social values to younger generations.




2017
-
Colombia and Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of): Work Songs of the Plains (Chants de travail des llanos)
For UNESCO, these songs, sung by the cattle ranchers of the Orinoco Plains, are an essential part of the daily life of llaneros (plainsmen) in Colombia and Venezuela. The songs are used to communicate with the animals and among workers, celebrating the deep connection between humans, animals, and the vast plains. -
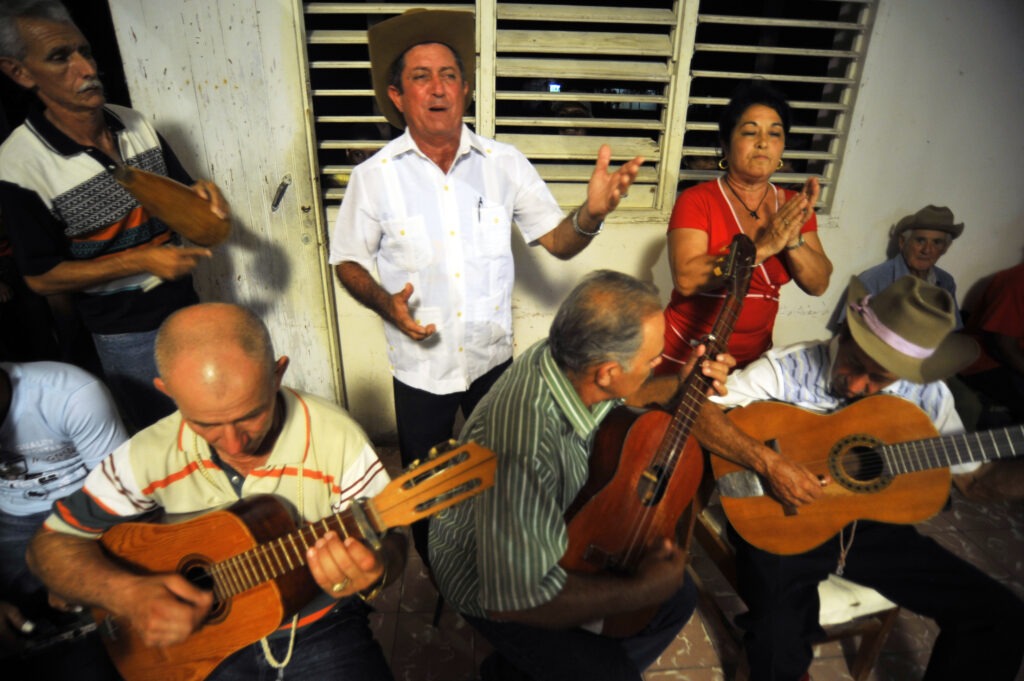
Cuba: Punto
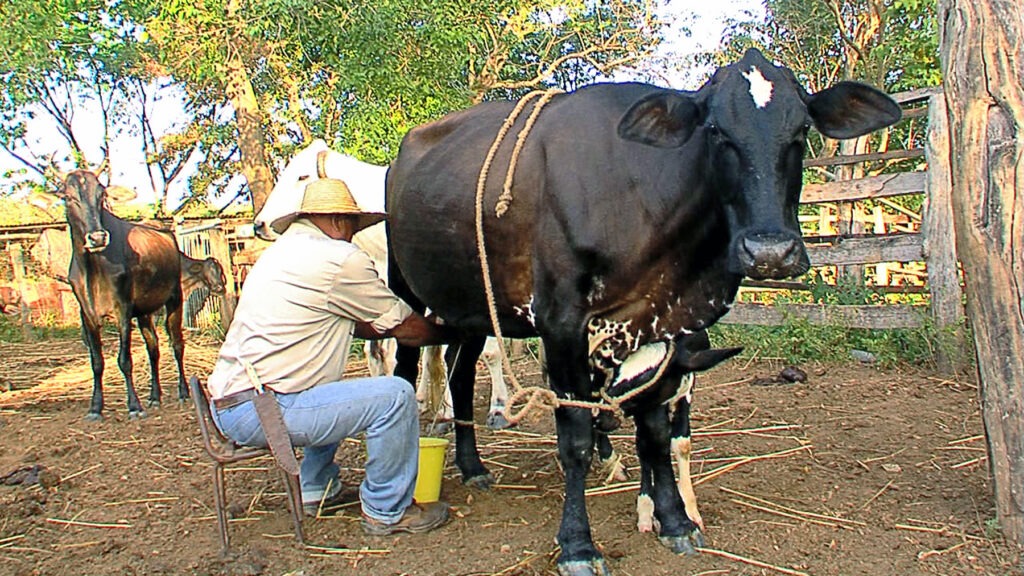
Punto is a traditional Cuban music genre combining poetic lyrics with melodies played on stringed instruments. Originating from Spanish peasant music, it is often performed in community gatherings and has become a key part of Cuban cultural identity, symbolizing a deep connection to the land and rural life. -
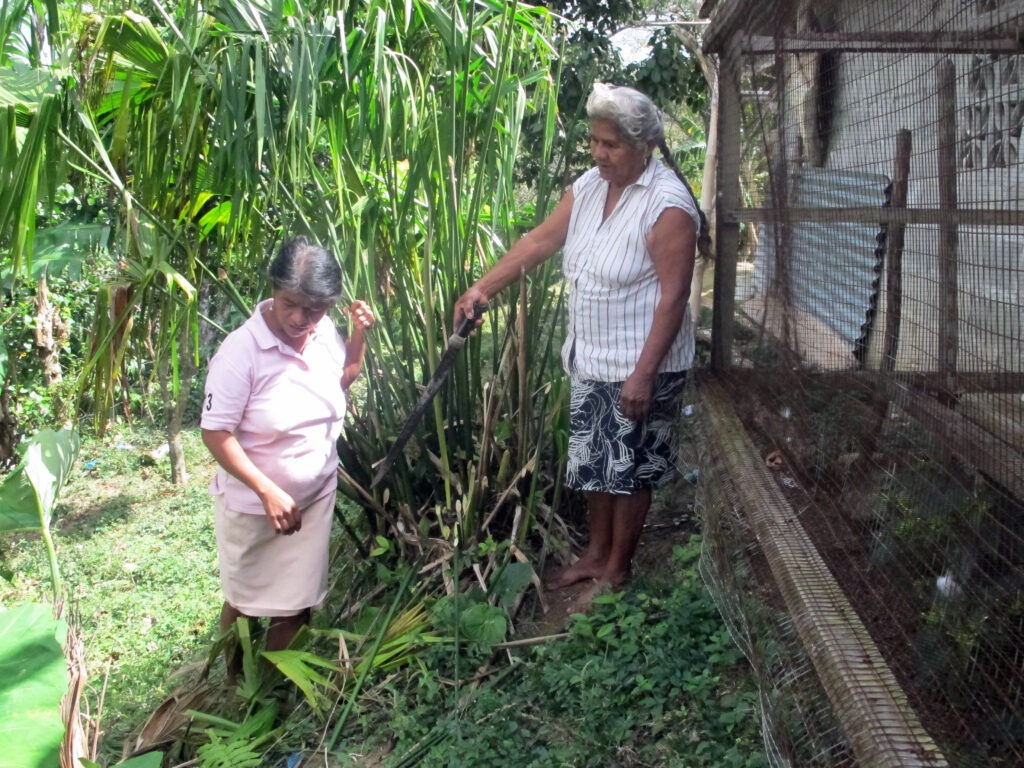
Panama: Techniques for Weaving Talco Hats and Pintas
This tradition involves intricate craftsmanship in the weaving of talco hats, crinejas, and pintas, often made from plant fibers. The practice is passed down from generation to generation, ensuring the preservation of the craft and its cultural significance in Panama.



2018
-
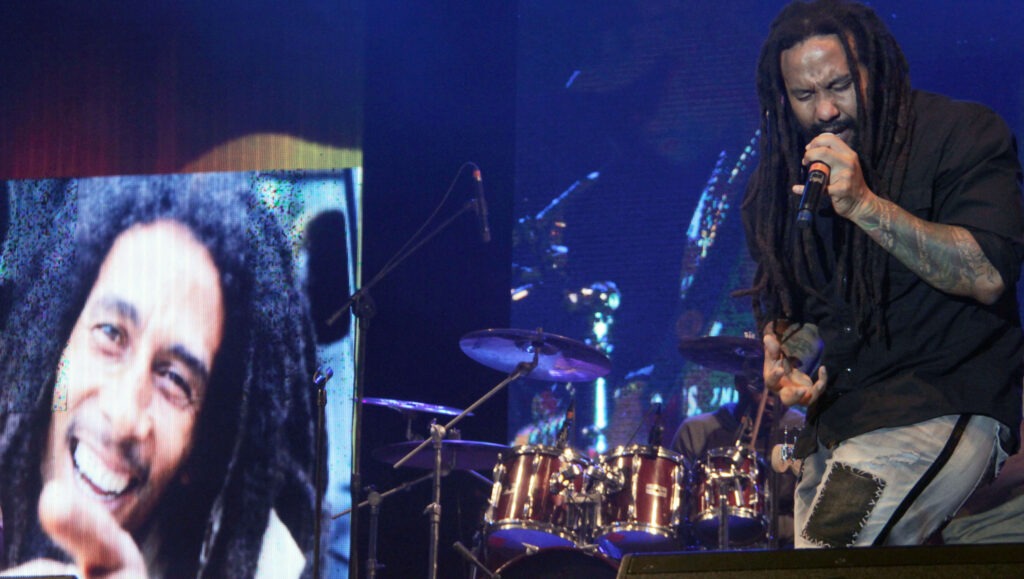
Jamaica: Reggae Music
For UNESCO, Reggae, synonymous with Jamaica, is more than just music; it is a cultural force that promotes messages of peace, love, and resistance. Popularized by icons like Bob Marley, reggae’s rhythms and messages have influenced people worldwide, while remaining deeply rooted in the island’s African traditions. -
Panama: Expressions and Rituals of Congo Culture
In Panama, the Afro-descendant Congo culture is celebrated through songs, dances, and rituals. These practices are not only a form of entertainment but also acts of resistance, passed down from enslaved Africans to their descendants. Congo rituals are performed in festivals that remember the struggles of the African diaspora and the fight for freedom. -
Cuba: Parrandas (Traditional Cuban Festivals)
Originating in central Cuba, parrandas are lively celebrations that mix music, dance, and fireworks. These festivals bring communities together to celebrate their shared identity and provide a stage for collective creativity. - Mexico: La Romería, Ritual Pilgrimage Cycle
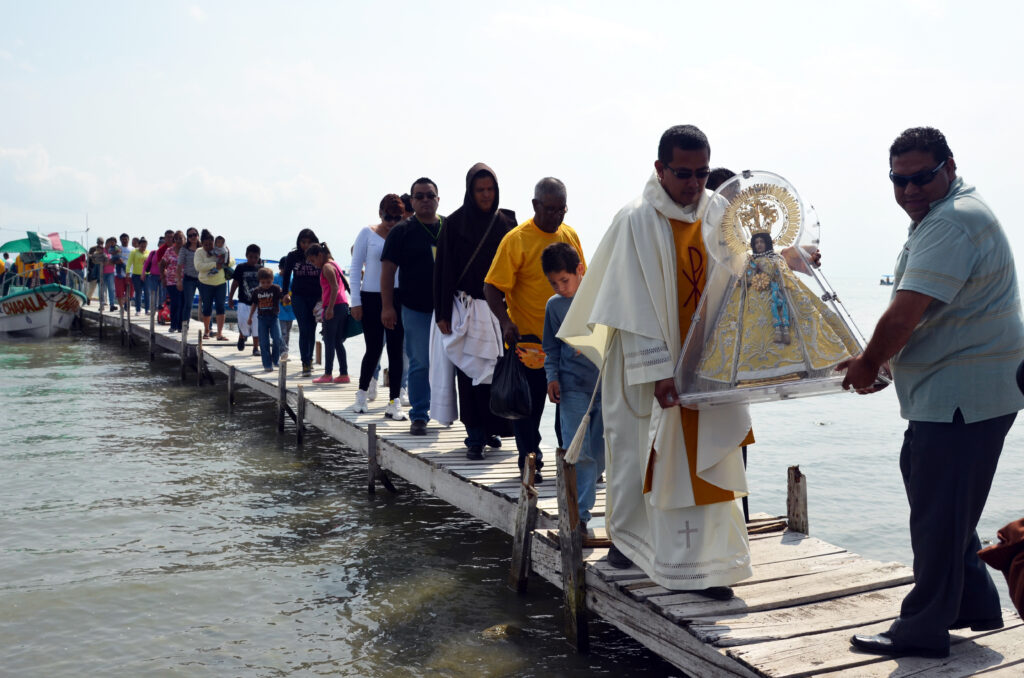
La Romería is a deeply rooted annual tradition celebrated on October 12 in honor of the Virgin of Zapopan, culminating a ritual cycle with over two million participants, vibrant indigenous dances, and community activities that strengthen social ties.




2019
-
Dominican Republic: Music and Dance of Bachata
For UNESCO, Bachata, known for its romantic lyrics and soulful melodies, is an iconic genre in the Dominican Republic. Rooted in rural life, it has evolved from humble beginnings into a symbol of Dominican identity, blending African, European, and indigenous influences to create a unique sound. -
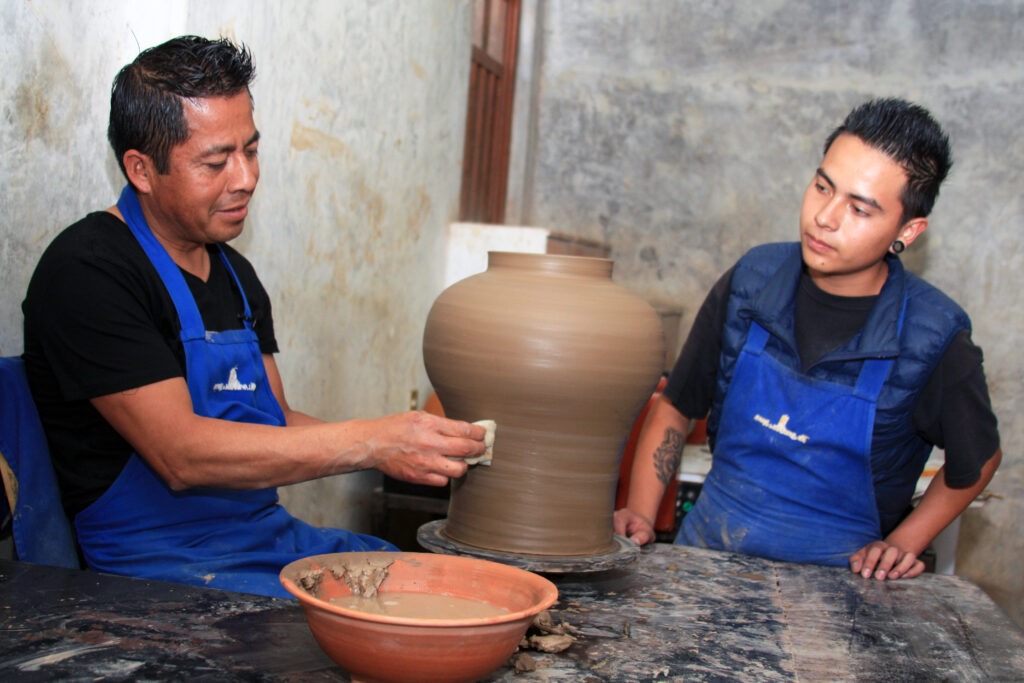
Mexico: Artisanal Talavera Pottery
The process of making Talavera pottery in Puebla (Mexico) and Spain is a centuries-old tradition that requires skill and patience. The vibrant designs and intricate patterns reflect the cultural exchange between the two regions, making it a symbol of shared heritage. -
Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of): Biocultural Program for the Safeguarding of the Palm Tradition
This program aims to preserve the knowledge and practices associated with the harvesting and processing of the blessed palm (palma bendita) in Venezuela. The program helps maintain local traditions while promoting environmental sustainability. - Colombia: Strategy for Safeguarding Traditional Crafts for Peacebuilding
This strategy aims to preserve traditional crafts through intergenerational knowledge transmission and practical learning, empowering vulnerable youth and fostering cultural entrepreneurship to contribute to peacebuilding and social inclusion.
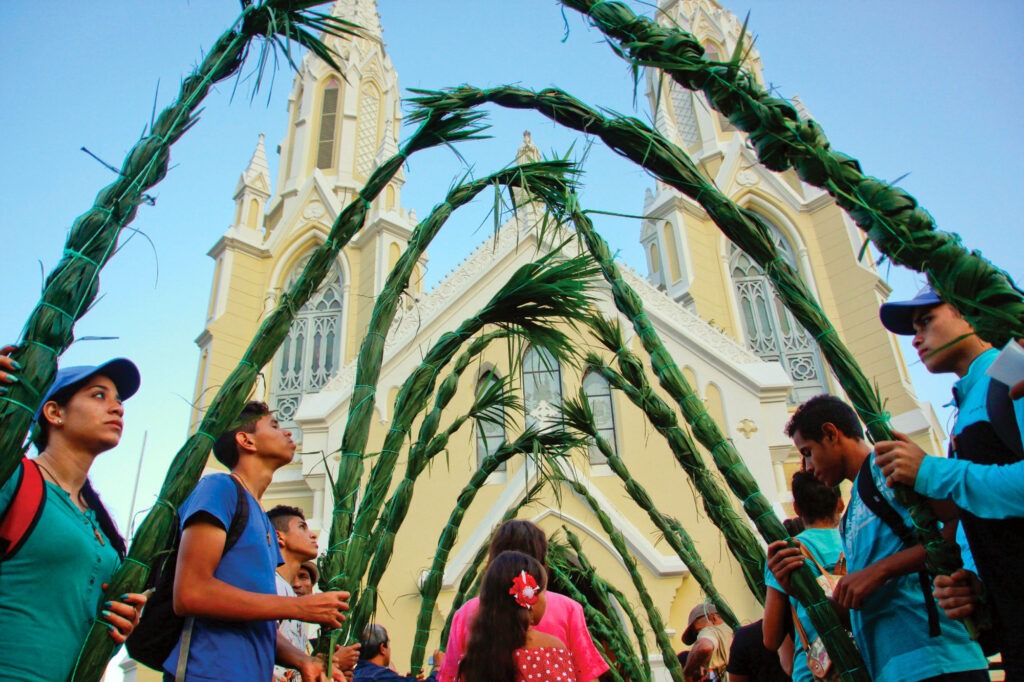
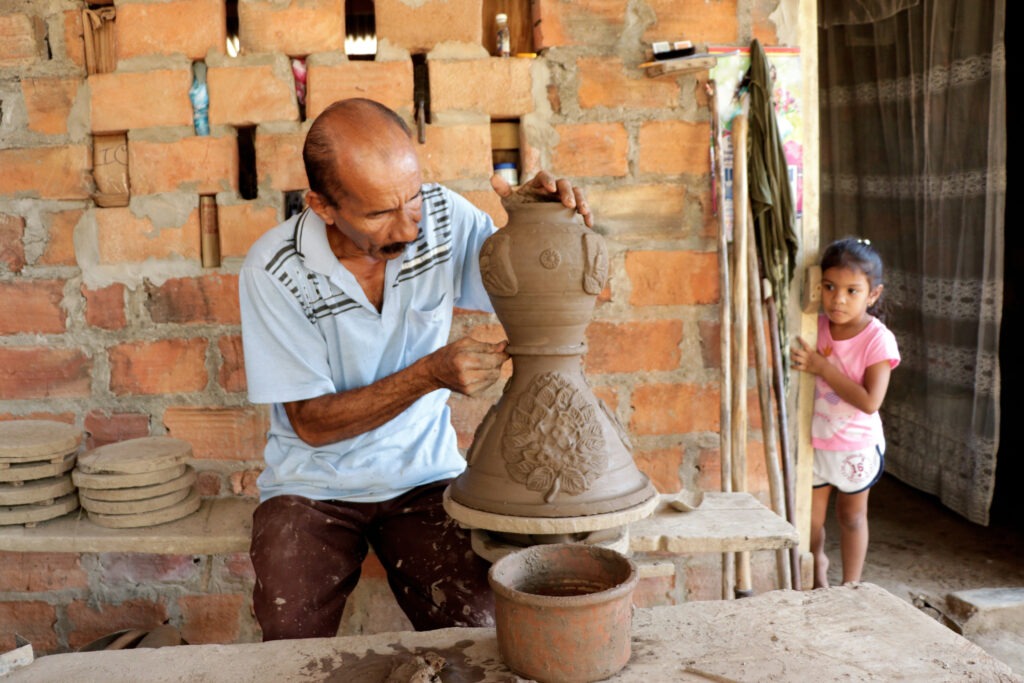
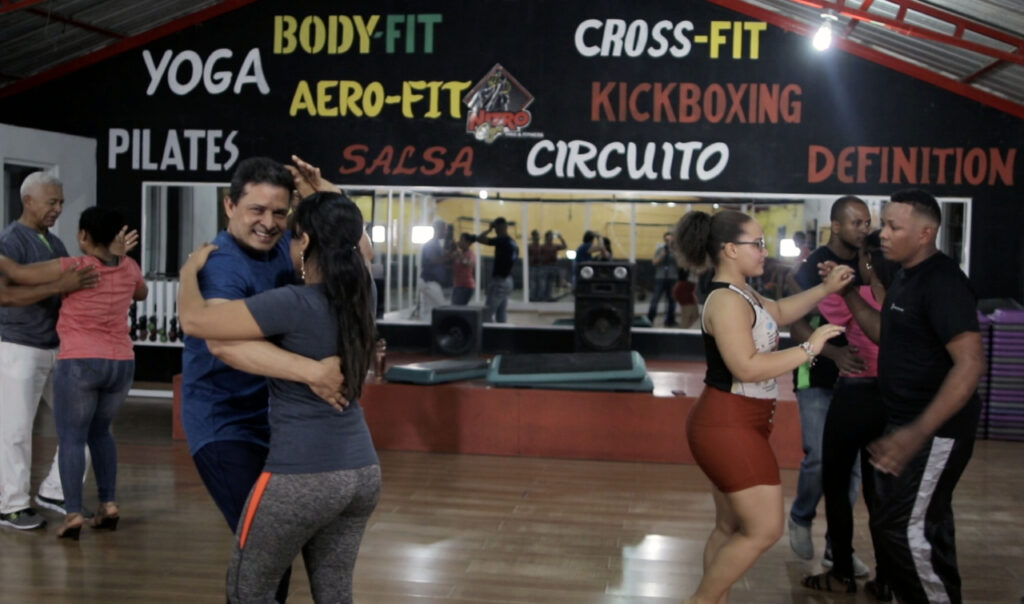



The cultural practices recognized by UNESCO from 2016 to 2019 showcase the diversity and complexity of Caribbean heritage. From music and dance to traditional craftsmanship, these elements highlight the importance of preserving cultural practices that define national identities. In our final article, we will explore the UNESCO recognitions from 2020 to 2023, further unveiling the rich heritage of the Caribbean region.
The Roots of Caribbean Intangible Heritage (2008-2013)
From 2008 to 2011, several Caribbean cultural elements were recognized as intangible cultural heritage by UNESCO. This recognition emphasized the region’s rich traditions, many of which are a testament to its diverse history, from indigenous customs to the impact of African, European, and other influences.
2008
Nicaragua: El Güegüense
One of the oldest theatrical performances in the Americas, El Güegüense is a satirical drama that blends indigenous and colonial Spanish elements. It reflects Nicaraguan resistance to colonial rule and is celebrated for its witty dialogue, vibrant costumes, and musical accompaniment.Dominican Republic: The Fraternity of the Holy Spirit of Villa Mella
This religious brotherhood maintains African cultural practices in the Dominican Republic through its vibrant processions and rituals. The Fraternity’s performances of sacred music and the use of traditional instruments, such as the congos, are vital to the preservation of African cultural identity in the Caribbean.Colombia: Palenque de San Basilio
Recognized as the first free town of enslaved Africans in the Americas, San Basilio preserves its unique language, customs, and traditions. Its residents have managed to keep their African roots alive, making it a significant cultural and historical site in Colombia.Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua: Garifuna Language, Dance, and Music
The Garifuna people, descendants of indigenous Carib and Arawak populations mixed with Africans, have a rich cultural tradition. Their language, music, and dance embody their struggles and resilience, especially their punta music, a vibrant expression of their identity.
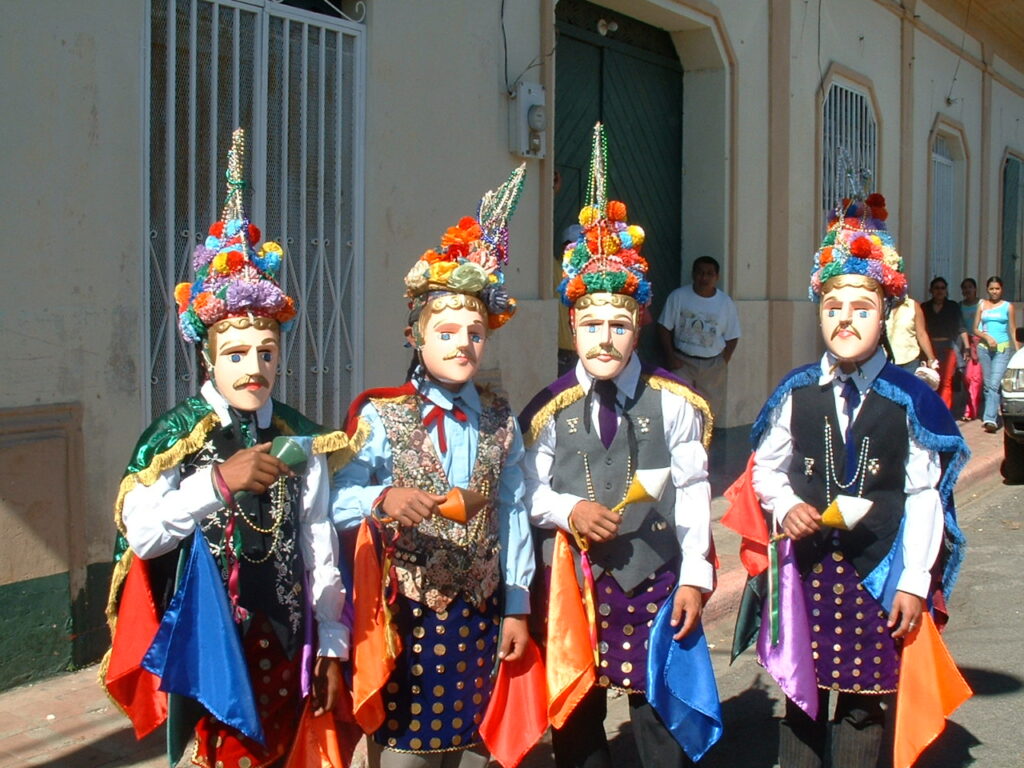
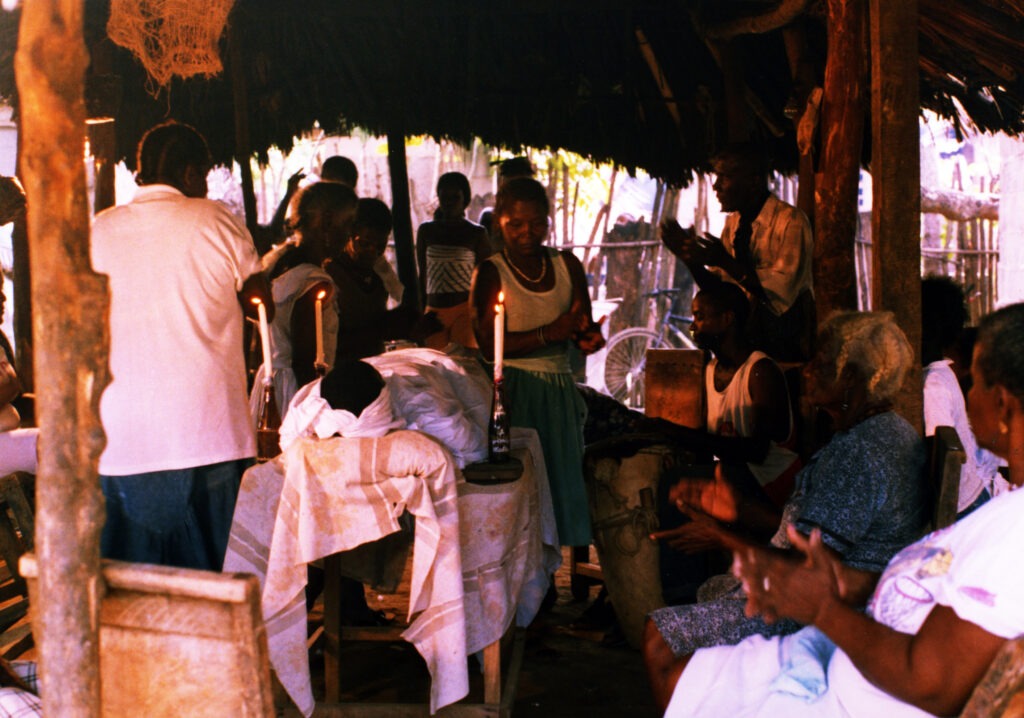
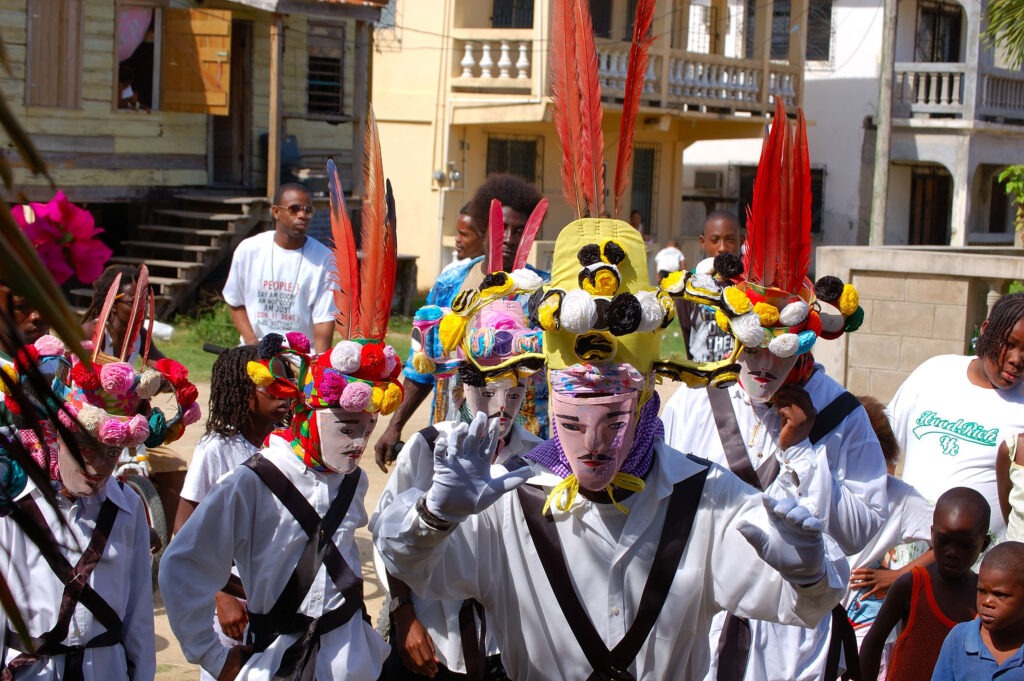




Dominican Republic: Cocolo Dance Theatre
The Cocolo dance theatre tradition originated among the descendants of British Caribbean slaves in the mid-19th century. This vibrant cultural expression blends African and European elements and is celebrated through annual performances during Christmas and Carnival.Guatemala: The Rabinal Achí Dance Theatre Tradition
The Rabinal Achí is a 15th-century Maya dynastic drama that reflects pre-Hispanic traditions and is presented through masked dances and theatrical performances. Danced annually on January 25th for Saint Paul, it connects the living with their ancestors, emphasizing cultural heritage and continuity.Cuba: The Tumba Francesa Dance Tradition
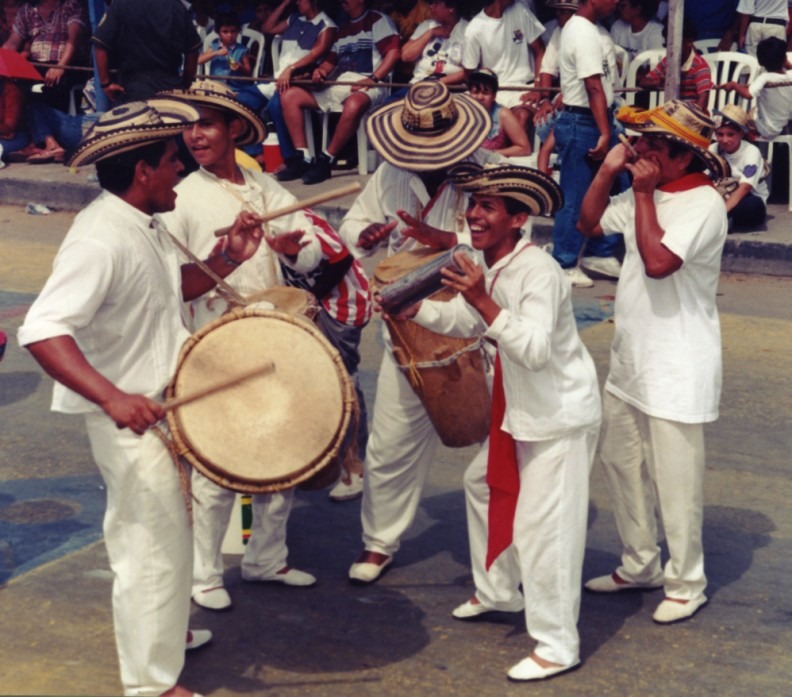
The Tumba Francesa, meaning “French drum,” is a dance, song, and drumming style imported to Cuba by Haitian slaves in the 1790s and reflects the Afro-Haitian heritage of the Oriente province. It is characterized by a fusion of Dahomey music from West Africa and traditional French dances, featuring vibrant performances led by a singer and accompanied by distinct hand-played drums and dancers in colonial-style dresses.Colombia: The Barranquilla Carnival
The Barranquilla Carnival, celebrated annually for four days before Lent, features a vibrant mix of dances and music from various Colombian cultures, reflecting the city’s rich heritage. This fusion of indigenous, European, and African traditions is showcased through lively performances, colorful costumes, and satirical songs that engage the community and celebrate contemporary life..
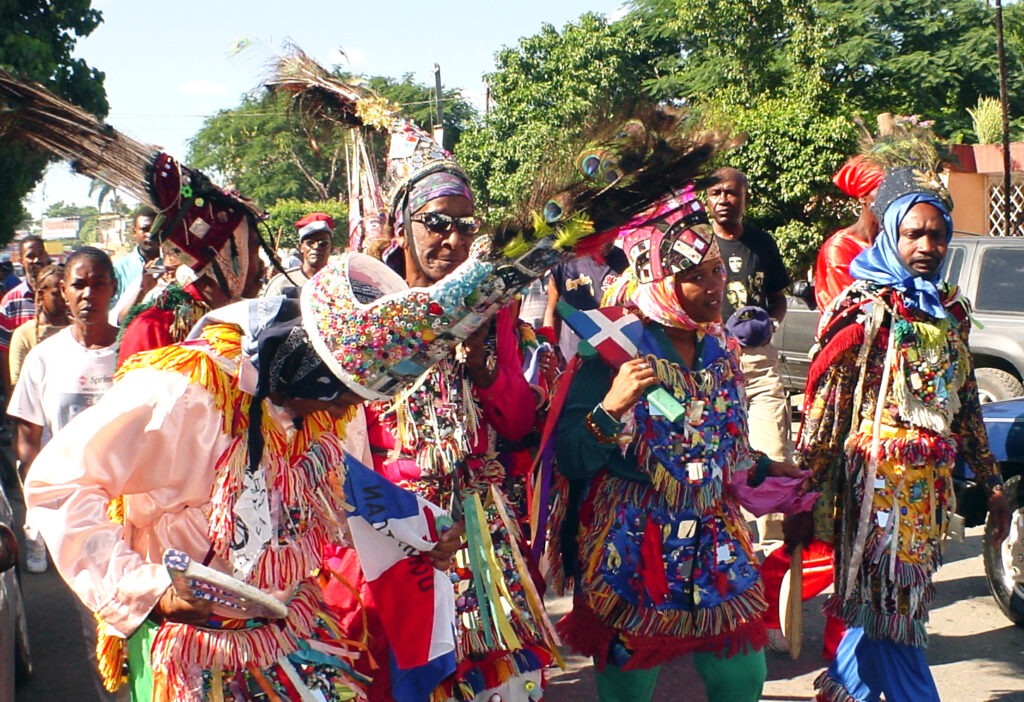
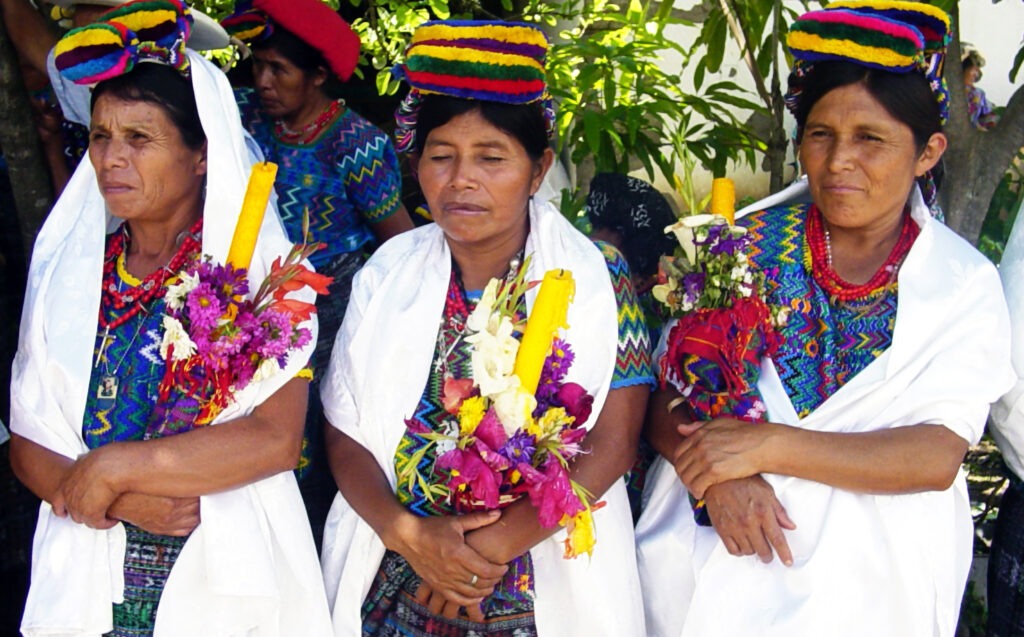




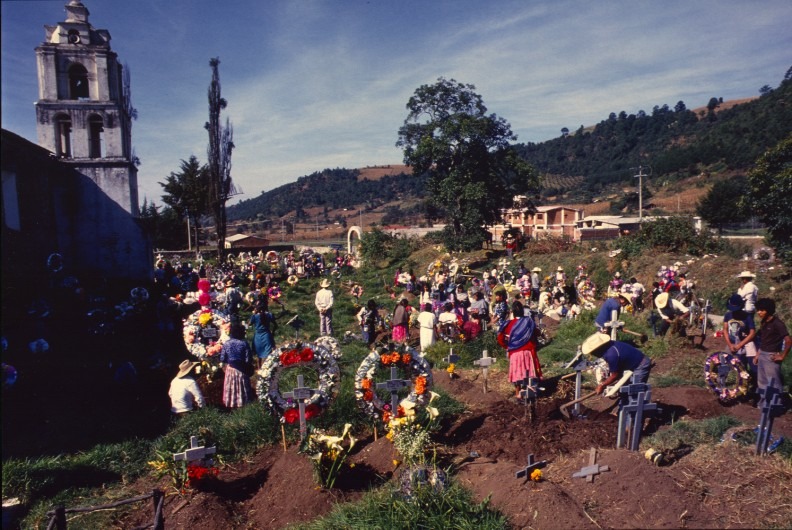
Mexico: Indigenous Festivals Dedicated to the Dead
El Día de los Muertos (Day of the Dead) is celebrated by indigenous communities in Mexico as a way to honor the temporary return of deceased loved ones, with festivities occurring from late October to early November. Families prepare altars with offerings and favorite foods of the departed, reflecting a blend of pre-Hispanic and Catholic traditions that strengthens community ties and cultural identity.Jamaica: The Traditions of the Maroons of Moore Town
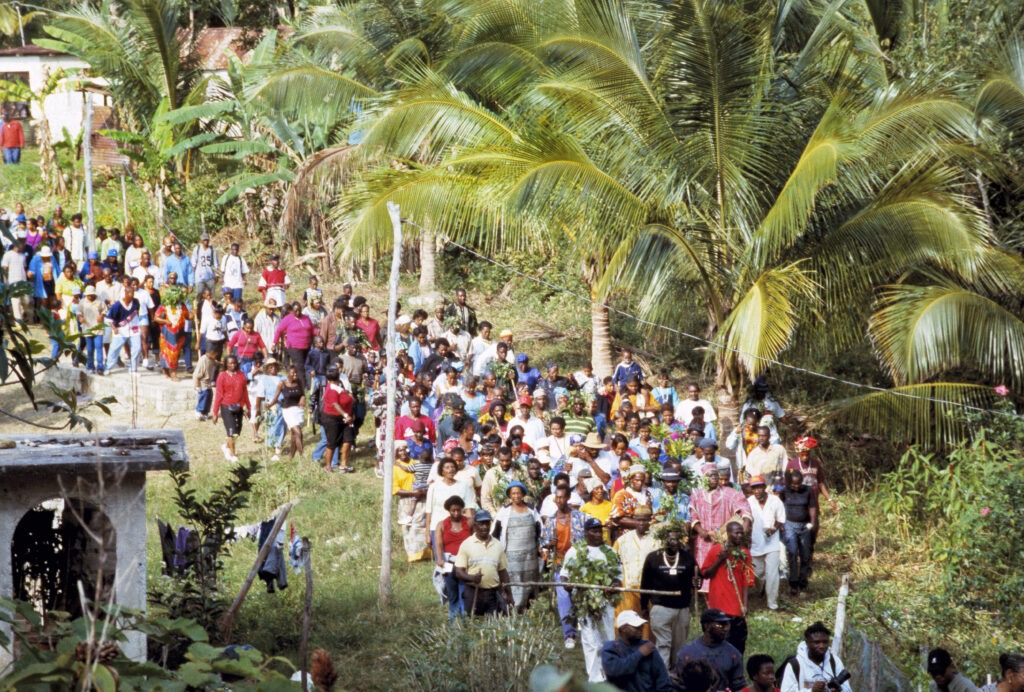
The Maroons of Moore Town, descendants of escaped enslaved Africans, have preserved a unique cultural heritage that includes the Kromanti Play, a blend of African traditions expressed through dance, music, and rituals honoring their ancestors. Despite facing opposition from missionaries and economic challenges, these traditions remain central to the identity and resilience of the Maroon community.Costa Rica: Pastoral Traditions and Ox-Carts
The traditional ox-cart, known as the carreta, is a celebrated symbol of Costa Rican culture, originally used to transport coffee and adorned with vibrant regional designs. Despite their decline in practical use, these intricately decorated carts remain a cherished representation of the country’s rural heritage and are featured prominently in festivals and parades.



2009
Colombia: Carnaval de Negros y Blancos
Celebrated in the city of Pasto, this carnival brings together people of different ethnicities to celebrate cultural diversity. It symbolizes the unity of all races and features colorful parades, elaborate costumes, and traditional dances.Colombia: Processions of the Holy Week in Popayán
One of the oldest religious traditions in Latin America, these processions are marked by reverence and devotion. Participants carry religious icons through the streets, maintaining a solemn atmosphere as the community honors their faith.Mexico: Ceremony of the Voladores
This ancient Mesoamerican ritual involves performers climbing a tall pole and spinning towards the ground, mimicking the descent of birds. It is a spiritual act meant to honor the gods and seek blessings for fertility and a good harvest.
- Mexico: Otomí-Chichimeca Heritage
The Otomí-Chichimeca people of Querétaro honor their connection to the land through annual pilgrimages to sacred sites like Peña de Bernal, praying for water and ancestral blessings. Their vibrant traditions and rituals are essential to their cultural identity.
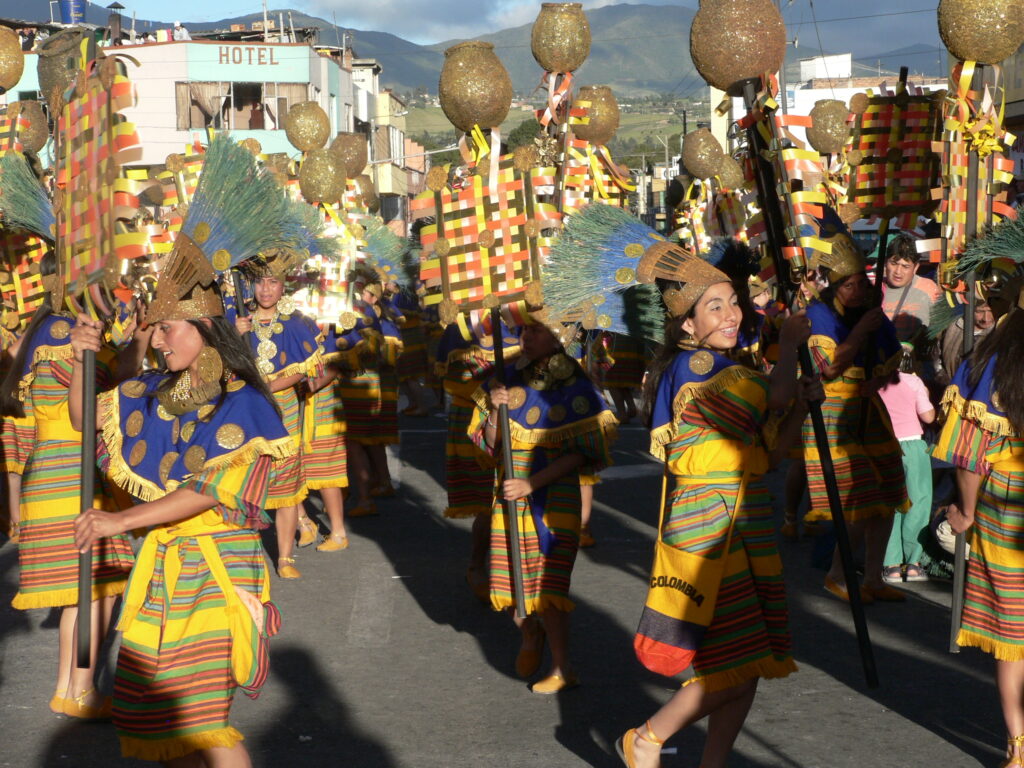
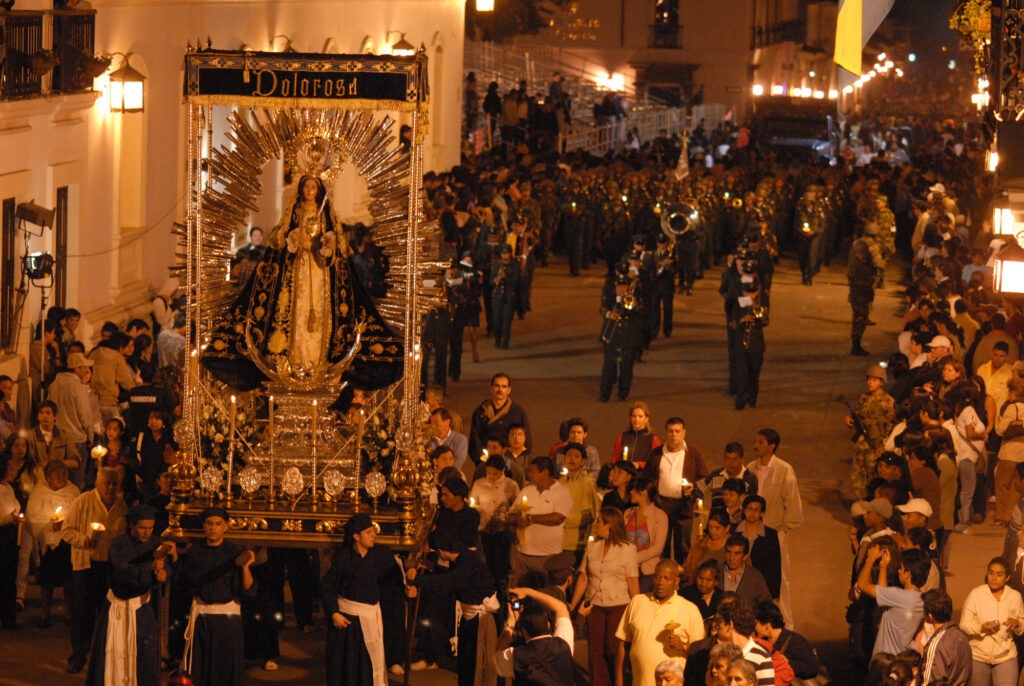
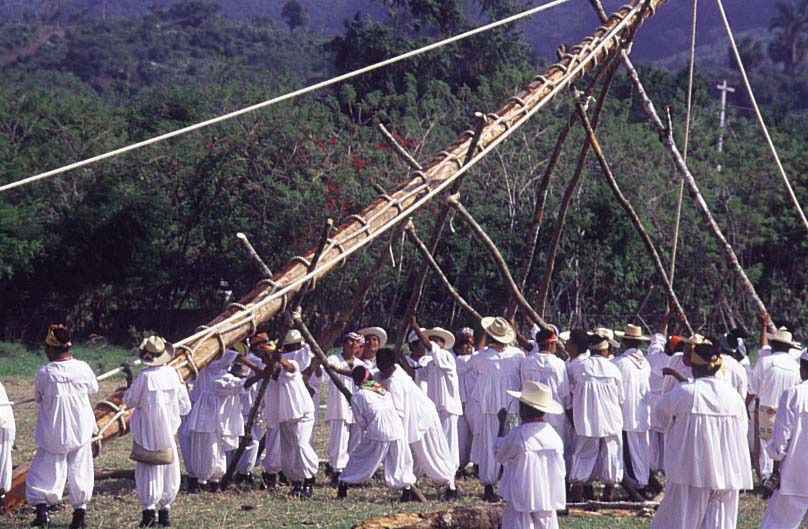




2010
Mexico: Traditional Mexican Cuisine
Recognized for its intricate methods of preparation and the role it plays in community-building, Traditional Mexican Cuisine reflects a harmonious relationship between people and nature. Corn, beans, and chili form the holy trinity of ingredients central to Mexican cuisine.Colombia: Wayuu Normative System
The Wayuu people, an indigenous group in the northern part of Colombia, have maintained their own legal system for centuries. This system promotes conflict resolution through dialogue, with spiritual leaders playing an important role in maintaining harmony within the community.Mexico: Pirekua
A traditional music genre of the Purépecha people in Michoacán, Pirekua is known for its poetic lyrics that express emotions ranging from love to mourning. Its slow tempo and melodic structure have been passed down through generations as a way of preserving their cultural heritage.
- Mexico: Parachicos in the Traditional Festival of Chiapa de Corzo
The traditional festival in Chiapa de Corzo, held annually from January 4 to 23, celebrates three Catholic saints with music, dance, and rituals, particularly honoring Saint Sebastian. The Parachicos dance, performed by masked dancers in colorful attire, serves as a collective offering and fosters mutual respect among the community.
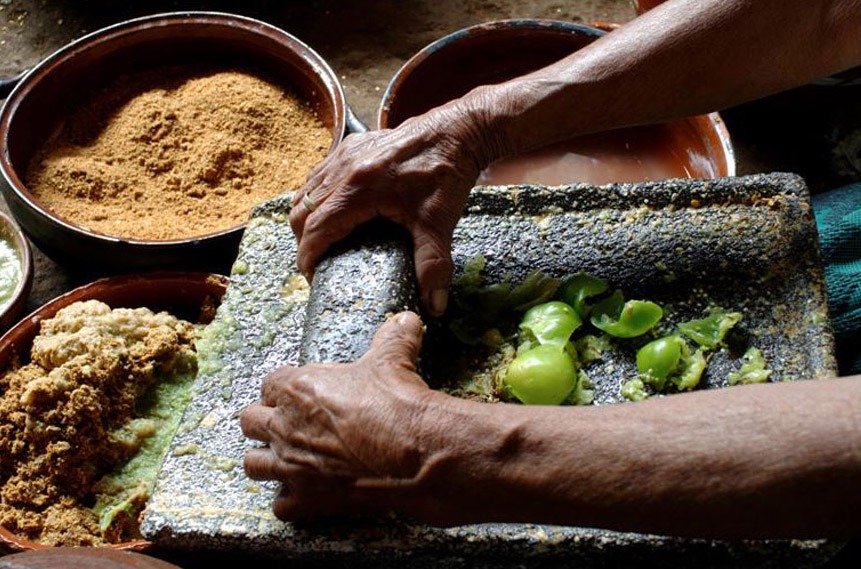
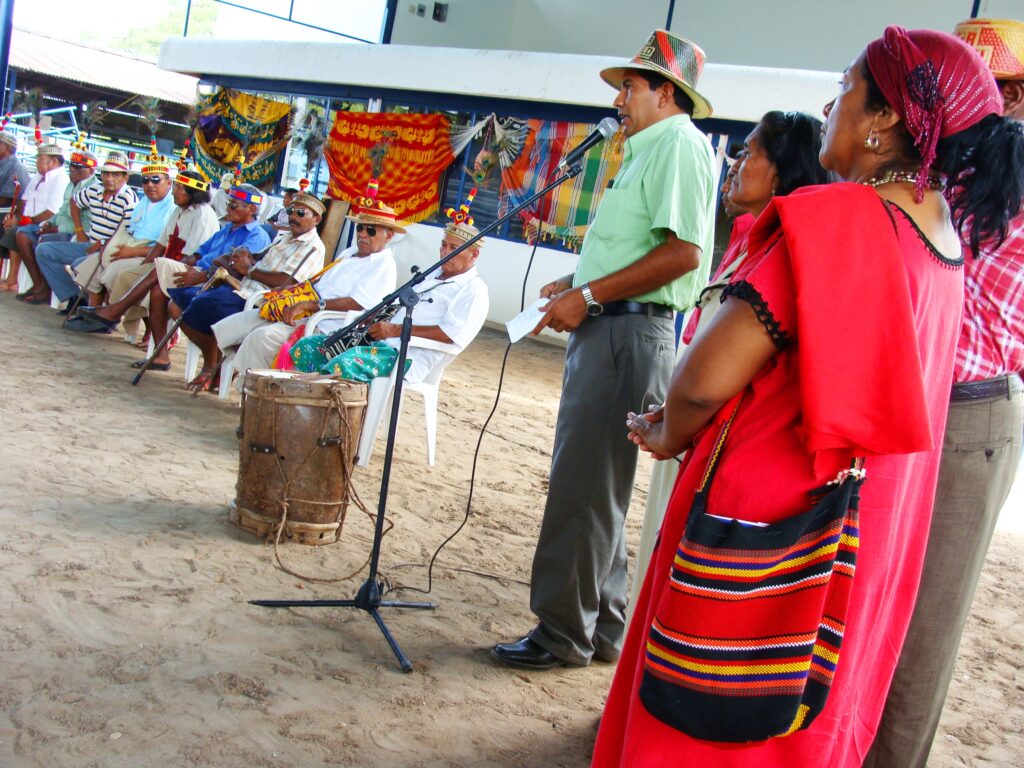
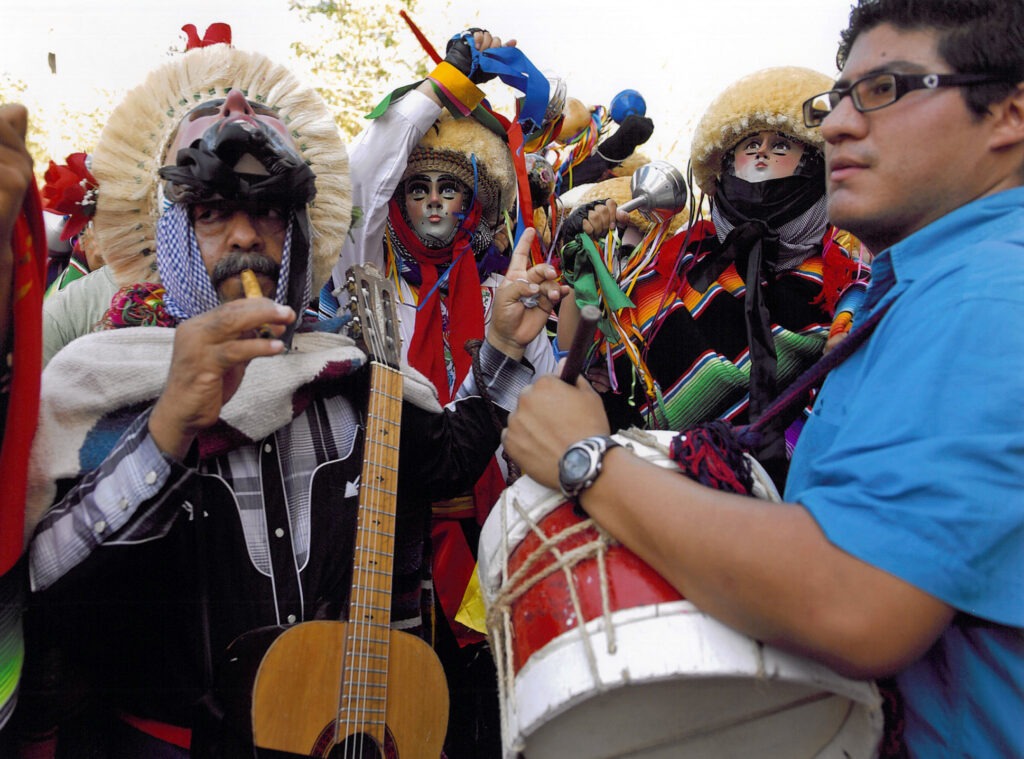




2011
Mexico: Mariachi
One of Mexico’s most recognizable cultural exports, Mariachi music is a blend of Spanish, indigenous, and African elements. It is traditionally performed at celebrations such as weddings, birthdays, and national holidays, with its vibrant rhythms and passionate lyrics captivating audiences worldwide.Colombia: Jaguar Shamans of Yuruparí
The shamans of the Yuruparí communities play a vital role in maintaining the balance between nature and humanity. Their rituals involve music, storytelling, and offerings to the jaguar, a sacred animal representing strength and wisdom.
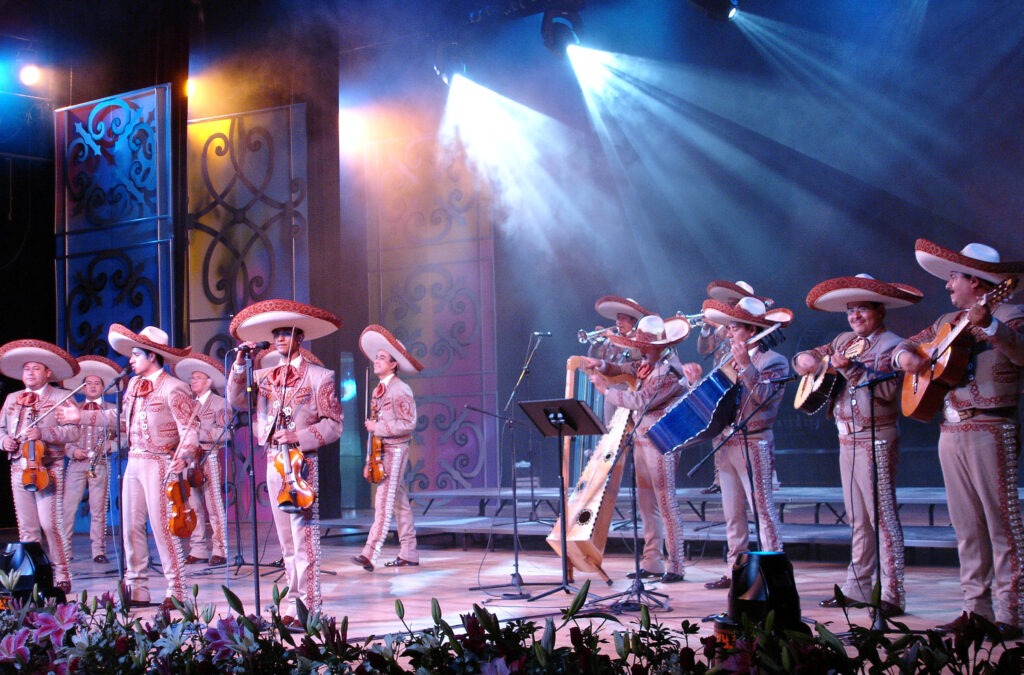
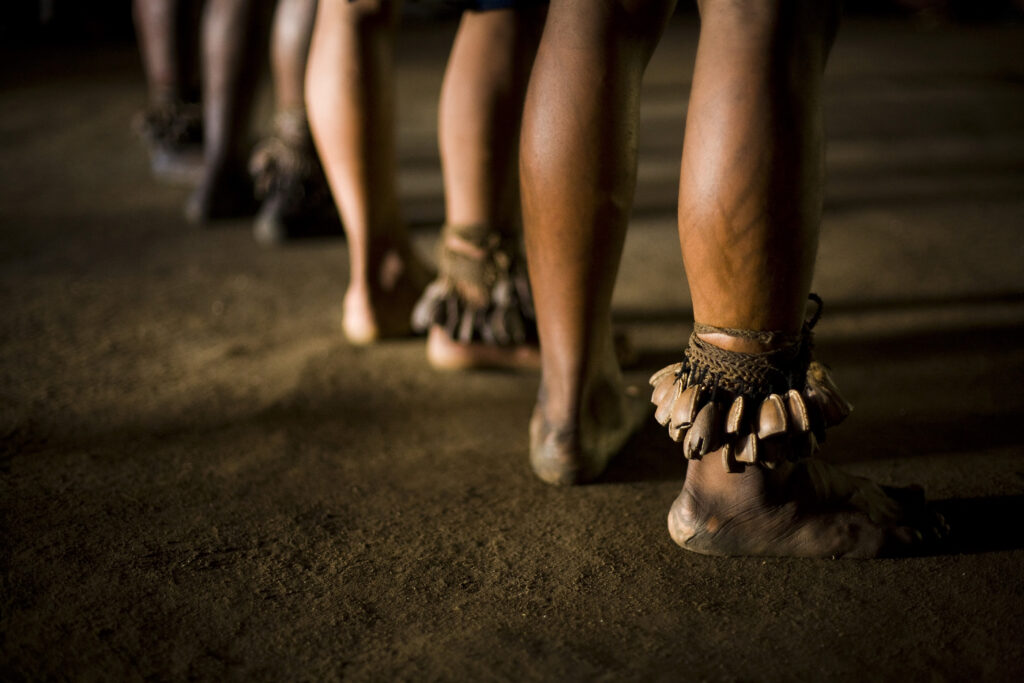


From the rich oral traditions of indigenous groups to the lively rhythms of musical performances, these UNESCO-recognized elements highlight the resilience and creativity of Caribbean cultures. In the next article, we will continue our journey, exploring more fascinating traditions recognized between 2012 and 2015.
Source: Dominican Today
Santo Domingo.- The Ministries of Culture and Foreign Affairs have announced that the Dominican Republic has been elected, for the first time, as a member of the Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of UNESCO, serving a four-year term.
This membership signifies the Dominican Republic’s commitment to preserving, promoting, and celebrating cultural traditions, arts, craftsmanship, and rituals from diverse cultures, which are primary goals of the Convention for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage.
Minister of Culture, Milagros Germán, described the country’s election as a historic achievement and an opportunity to showcase its cultural richness and diversity to the world.
Dominican Ambassador to UNESCO, Andrés L. Mateo, emphasized that this election is a testament to the collaborative efforts between the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MIREX), Ministry of Culture, the Permanent Mission of the Dominican Republic to UNESCO, and the Dominican National Commission for UNESCO. He highlighted their effective diplomatic strategy in building alliances and securing support from the international community.
The Dominican Republic, along with Haiti and Barbados, was elected by acclamation as a State Party to the Convention for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage, following a regional agreement within the Latin America and Caribbean group during the tenth session of the UNESCO General Assembly.
Minister Germán underscored that the country’s participation in this committee exemplifies its dedication to protecting and promoting its intangible cultural heritage, providing a platform to enhance its capabilities in this field.
About the Committee
The Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage is a UNESCO body comprising representatives from 24 states serving a four-year term. Its responsibilities include advancing the Convention’s objectives, advising on best practices, recommending measures for safeguarding intangible cultural heritage, managing funds for cultural preservation, proposing accreditation of non-governmental organizations to the General Assembly, and providing international assistance.


































